Crystal Structure of the Golgi-Associated Human Nα-Acetyltransferase 60 Reveals the Molecular Determinants for Substrate-Specific Acetylation
- PMID: 27320834
- PMCID: PMC4938767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2016.04.020
Crystal Structure of the Golgi-Associated Human Nα-Acetyltransferase 60 Reveals the Molecular Determinants for Substrate-Specific Acetylation
Abstract
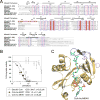
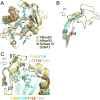
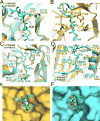
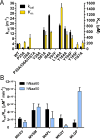
N-Terminal acetylation is a common and important protein modification catalyzed by N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs). Six human NATs (NatA-NatF) contain one catalytic subunit each, Naa10 to Naa60, respectively. In contrast to the ribosome-associated NatA to NatE, NatF/Naa60 specifically associates with Golgi membranes and acetylates transmembrane proteins. To gain insight into the molecular basis for the function of Naa60, we developed an Naa60 bisubstrate CoA-peptide conjugate inhibitor, determined its X-ray structure when bound to CoA and inhibitor, and carried out biochemical experiments. We show that Naa60 adapts an overall fold similar to that of the catalytic subunits of ribosome-associated NATs, but with the addition of two novel elongated loops that play important roles in substrate-specific binding. One of these loops mediates a dimer to monomer transition upon substrate-specific binding. Naa60 employs a catalytic mechanism most similar to Naa50. Collectively, these data reveal the molecular basis for Naa60-specific acetyltransferase activity with implications for its Golgi-specific functions.
Keywords: N-terminal acetylation; NAT; Naa60; NatF; acetyltransferase; crystal structure.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An organellar nα-acetyltransferase, naa60, acetylates cytosolic N termini of transmembrane proteins and maintains Golgi integrity.Cell Rep. 2015 Mar 3;10(8):1362-74. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.053. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25732826
-
Molecular determinants of the N-terminal acetyltransferase Naa60 anchoring to the Golgi membrane.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 21;292(16):6821-6837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770362. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28196861 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of human Naa60 (NatF), a Golgi-localized bi-functional acetyltransferase.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 23;6:31425. doi: 10.1038/srep31425. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27550639 Free PMC article.
-
NAA60 (HAT4): the newly discovered bi-functional Golgi member of the acetyltransferase family.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Dec 21;14(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01402-8. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36539894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-translational, Post-translational, and Non-catalytic Roles of N-Terminal Acetyltransferases.Mol Cell. 2019 Mar 21;73(6):1097-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.007. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30878283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein N-Terminal Acetylation: Structural Basis, Mechanism, Versatility, and Regulation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Jan;46(1):15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 32912665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical and structural analysis of N-terminal acetyltransferases.Methods Enzymol. 2019;626:271-299. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.07.016. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 31606079 Free PMC article.
-
Microscopy-based Saccharomyces cerevisiae complementation model reveals functional conservation and redundancy of N-terminal acetyltransferases.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 24;6:31627. doi: 10.1038/srep31627. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27555049 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for N-terminal alpha-synuclein acetylation by human NatB.Elife. 2020 Sep 4;9:e57491. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57491. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32885784 Free PMC article.
-
A Continuous Assay Set to Screen and Characterize Novel Protein N-Acetyltransferases Unveils Rice General Control Non-repressible 5-Related N-Acetyltransferase2 Activity.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 22;13:832144. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.832144. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35273627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksnes H, Hole K, Arnesen T. Molecular, cellular, and physiological significance of N-terminal acetylation. International review of cell and molecular biology. 2015a;316:267–305. - PubMed
-
- Aksnes H, Van Damme P, Goris M, Starheim KK, Marie M, Stove SI, Hoel C, Kalvik TV, Hole K, Glomnes N, et al. An organellar nalpha-acetyltransferase, naa60, acetylates cytosolic N termini of transmembrane proteins and maintains Golgi integrity. Cell reports. 2015b;10:1362–1374. - PubMed
-
- Arnesen T, Van Damme P, Polevoda B, Helsens K, Evjenth R, Colaert N, Varhaug JE, Vandekerckhove J, Lillehaug JR, Sherman F, et al. Proteomics analyses reveal the evolutionary conservation and divergence of N-terminal acetyltransferases from yeast and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:8157–8162. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

