African Swine Fever Epidemic, Poland, 2014-2015
- PMID: 27314611
- PMCID: PMC4918169
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2207.151708
African Swine Fever Epidemic, Poland, 2014-2015
Abstract
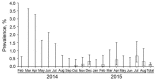
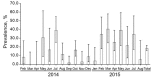
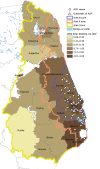
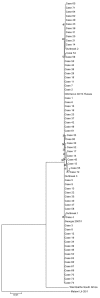
In Poland, African swine fever (ASF) emerged in February 2014; by August 2015, the virus had been detected in >130 wild boar and in pigs in 3 backyard holdings. We evaluated ASF spread in Poland during these 18 months. Phylogenetic analysis indicated repeated incursions of genetically distinct ASF viruses of genotype II; the number of cases positively correlated wild boar density; and disease spread was very slow. More cases were reported during summer than autumn. The 18-month prevalence of ASF in areas under various animal movement restrictions was 18.6% among wild boar found dead or killed by vehicles and only 0.2% in hunted wild boar. Repeated introductions of the virus into the country, the primary role of wild boar in virus maintenance, and the slow spread of the disease indicate a need for enhanced biosecurity at pig holdings and continuous and intensive surveillance for fast detection of ASF.
Keywords: African swine fever; Poland; epidemic; epidemiology; pigs; viruses; wild boar.
Figures

Similar articles
-
African swine fever in Latvian wild boar-A step closer to elimination.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020 Nov;67(6):2615-2629. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13611. Epub 2020 May 31. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020. PMID: 32372476
-
Do wild boar movements drive the spread of African Swine Fever?Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018 Dec;65(6):1588-1596. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12910. Epub 2018 May 25. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018. PMID: 29799177
-
Current status of African swine fever virus in a population of wild boar in eastern Poland (2014-2015).Arch Virol. 2016 Jan;161(1):189-95. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2650-5. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Arch Virol. 2016. PMID: 26497350 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever: Fast and Furious or Slow and Steady?Viruses. 2019 Sep 17;11(9):866. doi: 10.3390/v11090866. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31533266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nine Years of African Swine Fever in Poland.Viruses. 2023 Nov 27;15(12):2325. doi: 10.3390/v15122325. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Undetected Circulation of African Swine Fever in Wild Boar, Asia.Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;26(10):2480-2482. doi: 10.3201/eid2610.200608. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32946727 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Wildlife and Pests in the Transmission of Pathogenic Agents to Domestic Pigs: A Systematic Review.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 31;13(11):1830. doi: 10.3390/ani13111830. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
African Swine Fever Virus, Siberia, Russia, 2017.Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Apr;24(4):796-798. doi: 10.3201/eid2404.171238. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29553323 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and epitope analysis of monoclonal antibodies against African swine fever virus DP96R protein.BMC Vet Res. 2024 May 11;20(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04043-6. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38734611 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal clustering and Random Forest models to identify risk factors of African swine fever outbreak in Romania in 2018-2019.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 22;11(1):2098. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81329-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33483559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Organisation for Animal Health. World Animal Health Information Database (WAHID) [cited 2016 Apr 23]. http://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Wahidhome/Home
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

