Single-dose treatment with a humanized neutralizing antibody affords full protection of a human transgenic mouse model from lethal Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-coronavirus infection
- PMID: 27312105
- PMCID: PMC5109928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.06.003
Single-dose treatment with a humanized neutralizing antibody affords full protection of a human transgenic mouse model from lethal Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-coronavirus infection
Abstract
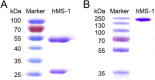
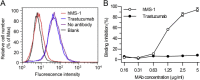
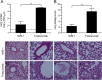
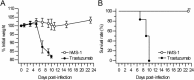
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is continuously spreading and causing severe and fatal acute respiratory disease in humans. Prophylactic and therapeutic strategies are therefore urgently needed to control MERS-CoV infection. Here, we generated a humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb), designated hMS-1, which targeted the MERS-CoV receptor-binding domain (RBD) with high affinity. hMS-1 significantly blocked MERS-CoV RBD binding to its viral receptor, human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (hDPP4), potently neutralized infection by a prototype MERS-CoV, and effectively cross-neutralized evolved MERS-CoV isolates through recognizing highly conserved RBD epitopes. Notably, single-dose treatment with hMS-1 completely protected hDPP4 transgenic (hDPP4-Tg) mice from lethal infection with MERS-CoV. Taken together, our data suggest that hMS-1 might be developed as an effective immunotherapeutic agent to treat patients infected with MERS-CoV, particularly in emergent cases.
Keywords: Humanized monoclonal antibody; Lethal infection; MERS-CoV; Protection; Receptor-binding domain; Treatment.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domains of Multiple Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (MERS-CoVs) Induce Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies against Divergent Human and Camel MERS-CoVs and Antibody Escape Mutants.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01651-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01651-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795425 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Nanobody Targeting Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Receptor-Binding Domain Has Potent Cross-Neutralizing Activity and Protective Efficacy against MERS-CoV.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00837-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00837-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950421 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant receptor-binding domain of MERS-CoV in trimeric form protects human dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (hDPP4) transgenic mice from MERS-CoV infection.Virology. 2016 Dec;499:375-382. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27750111 Free PMC article.
-
Development of human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for prevention and therapy of MERS-CoV infections.Microbes Infect. 2015 Feb;17(2):142-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Microbes Infect. 2015. PMID: 25456101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies as Promising Therapeutics against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection.Viruses. 2018 Nov 30;10(12):680. doi: 10.3390/v10120680. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30513619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Product of natural evolution (SARS, MERS, and SARS-CoV-2); deadly diseases, from SARS to SARS-CoV-2.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Jan 2;17(1):62-83. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1797369. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 32783700 Free PMC article.
-
A Human DPP4-Knockin Mouse's Susceptibility to Infection by Authentic and Pseudotyped MERS-CoV.Viruses. 2018 Aug 23;10(9):448. doi: 10.3390/v10090448. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30142928 Free PMC article.
-
MERS-CoV spike protein: a key target for antivirals.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Feb;21(2):131-143. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1271415. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 27936982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical outcomes among hospital patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 22;19(1):870. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4555-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31640578 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies and vaccines against Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):841-856. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1624482. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 31169078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boulianne G.L., Hozumi N., Shulman M.J. Production of functional chimaeric mouse/human antibody. Nature. 1984;312:643–646. - PubMed
-
- Corti D., Zhao J., Pedotti M., Simonelli L., Agnihothram S., Fett C., Fernandez-Rodriguez B., Foglierini M., Agatic G., Vanzetta F., Gopal R., Langrish C.J., Barrett N.A., Sallusto F., Baric R.S., Varani L., Zambon M., Perlman S., Lanzavecchia A. Prophylactic and postexposure efficacy of a potent human monoclonal antibody against MERS coronavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2015;112:10473–10478. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

