Chemical genetic discovery of PARP targets reveals a role for PARP-1 in transcription elongation
- PMID: 27256882
- PMCID: PMC5540732
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf7865
Chemical genetic discovery of PARP targets reveals a role for PARP-1 in transcription elongation
Abstract
Poly[adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerases (PARPs) are a family of enzymes that modulate diverse biological processes through covalent transfer of ADP-ribose from the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) onto substrate proteins. Here we report a robust NAD(+) analog-sensitive approach for PARPs, which allows PARP-specific ADP-ribosylation of substrates that is suitable for subsequent copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reactions. Using this approach, we mapped hundreds of sites of ADP-ribosylation for PARPs 1, 2, and 3 across the proteome, as well as thousands of PARP-1-mediated ADP-ribosylation sites across the genome. We found that PARP-1 ADP-ribosylates and inhibits negative elongation factor (NELF), a protein complex that regulates promoter-proximal pausing by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). Depletion or inhibition of PARP-1 or mutation of the ADP-ribosylation sites on NELF-E promotes Pol II pausing, providing a clear functional link between PARP-1, ADP-ribosylation, and NELF. This analog-sensitive approach should be broadly applicable across the PARP family and has the potential to illuminate the ADP-ribosylated proteome and the molecular mechanisms used by individual PARPs to mediate their responses to cellular signals.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
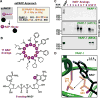



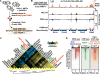

Comment in
-
Post-translational modifications: ADP-ribosylation promotes transcription elongation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jun 22;17(7):397. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.83. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27329964 No abstract available.
-
Identification of PARP-Specific ADP-Ribosylation Targets Reveals a Regulatory Function for ADP-Ribosylation in Transcription Elongation.Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 21;63(2):181-183. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.006. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27447982
Similar articles
-
Identifying Direct Protein Targets of Poly-ADP-Ribose Polymerases (PARPs) Using Engineered PARP Variants-Orthogonal Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) Analog Pairs.Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 1;7(2):121-39. doi: 10.1002/9780470559277.ch140259. Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26344237 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Protein Substrates of Specific PARP Enzymes Using Analog-Sensitive PARP Mutants and a "Clickable" NAD+ Analog.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1608:111-135. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6993-7_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28695507 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of PARP-Specific ADP-Ribosylation Targets Reveals a Regulatory Function for ADP-Ribosylation in Transcription Elongation.Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 21;63(2):181-183. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.006. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27447982
-
Chemical genetic methodologies for identifying protein substrates of PARPs.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 May;47(5):390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34366182 Review.
-
The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:3046-82. doi: 10.2741/2909. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981777 Review.
Cited by
-
PARP1 activation increases expression of modified tumor suppressors and pathways underlying development of aggressive hepatoblastoma.Commun Biol. 2018 Jun 11;1:67. doi: 10.1038/s42003-018-0077-8. eCollection 2018. Commun Biol. 2018. PMID: 30271949 Free PMC article.
-
PARP inhibitor shuts down the global translation of thyroid cancer through promoting Pol II binding to DIMT1 pause.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;19(12):3970-3986. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.81895. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37564214 Free PMC article.
-
ELTA: Enzymatic Labeling of Terminal ADP-Ribose.Mol Cell. 2019 Feb 21;73(4):845-856.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.12.022. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30712989 Free PMC article.
-
Bump-and-Hole Engineering Identifies Specific Substrates of Glycosyltransferases in Living Cells.Mol Cell. 2020 Jun 4;78(5):824-834.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.030. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32325029 Free PMC article.
-
PARP3 is a promoter of chromosomal rearrangements and limits G4 DNA.Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 27;8:15110. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15110. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28447610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibson BA, Kraus WL. New insights into the molecular and cellular functions of poly(ADP-ribose) and PARPs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:411. - PubMed
-
- Hottiger MO. Nuclear ADP-ribosylation and its role in chromatin plasticity, cell differentiation, and epigenetics. Annu Rev Biochem. 2015;84:227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

