Targeting histone methyltransferases and demethylases in clinical trials for cancer therapy
- PMID: 27222667
- PMCID: PMC4877953
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0223-4
Targeting histone methyltransferases and demethylases in clinical trials for cancer therapy
Abstract
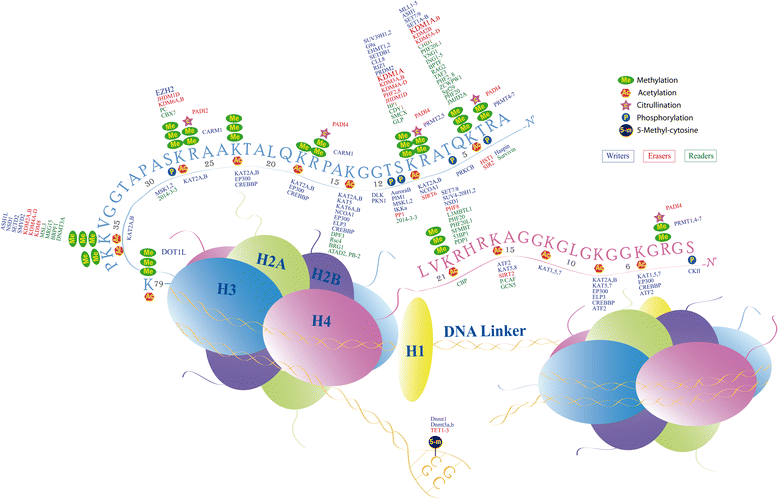
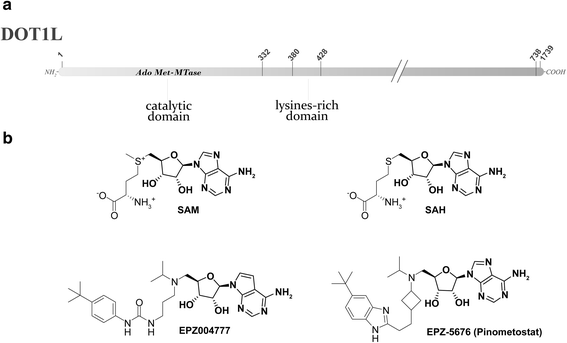
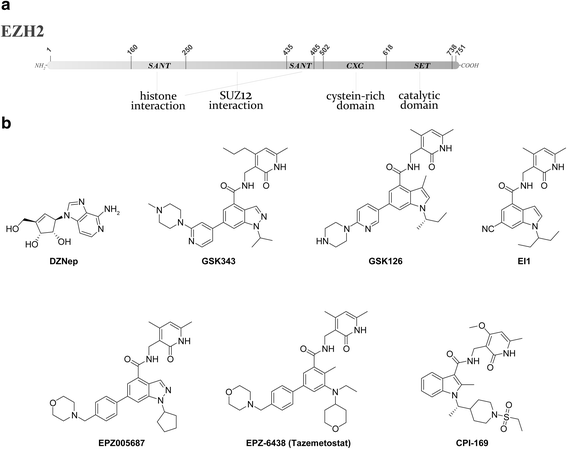
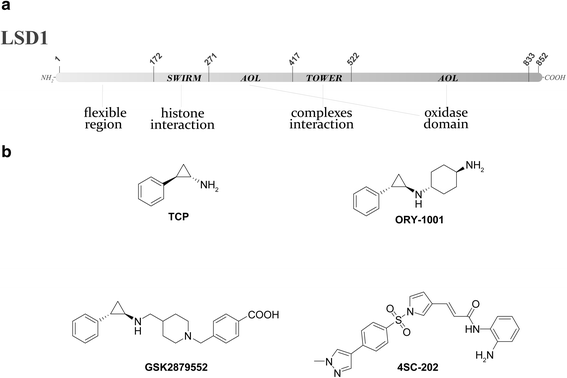
The term epigenetics is defined as heritable changes in gene expression that are not due to alterations of the DNA sequence. In the last years, it has become more and more evident that dysregulated epigenetic regulatory processes have a central role in cancer onset and progression. In contrast to DNA mutations, epigenetic modifications are reversible and, hence, suitable for pharmacological interventions. Reversible histone methylation is an important process within epigenetic regulation, and the investigation of its role in cancer has led to the identification of lysine methyltransferases and demethylases as promising targets for new anticancer drugs. In this review, we describe those enzymes and their inhibitors that have already reached the first stages of clinical trials in cancer therapy, namely the histone methyltransferases DOT1L and EZH2 as well as the demethylase LSD1.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Demethylase inhibitors; Epigenetics; Histone demethylase; Histone methyltransferase; Histone modifications; Lysine methylation; Methylome; Methyltransferase inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Histone Methylation in Cancer.Cancer J. 2017 Sep/Oct;23(5):292-301. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000283. Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 28926430 Review.
-
Targeting epigenetic regulators for cancer therapy: modulation of bromodomain proteins, methyltransferases, demethylases, and microRNAs.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016 Jul;20(7):783-99. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1134490. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26799480 Review.
-
The emerging therapeutic potential of histone methyltransferase and demethylase inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2009 Oct;4(10):1568-82. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900301. ChemMedChem. 2009. PMID: 19739196 Review.
-
Targeting histone lysine methylation in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jun;150:1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25578037 Review.
-
Histone modification therapy of cancer.Adv Genet. 2010;70:341-86. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380866-0.60013-7. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 20920755 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the epigenome in in-stent restenosis: from mechanisms to therapy.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Jan 26;23:1136-1160. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.024. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 33664994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Modifications and Non-Coding RNAs: Mutual Epigenetic Regulation and Role in Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5801. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105801. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of T cell differentiation and function by epigenetic modification enzymes.Semin Immunopathol. 2019 May;41(3):315-326. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00731-w. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 30963214 Review.
-
Context-Dependent Functions of KDM6 Lysine Demethylases in Physiology and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1433:139-165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-38176-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37751139
-
The Jumonji-C oxygenase JMJD7 catalyzes (3S)-lysyl hydroxylation of TRAFAC GTPases.Nat Chem Biol. 2018 Jul;14(7):688-695. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0071-y. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Nat Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29915238 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

