A clickable glutathione approach for identification of protein glutathionylation in response to glucose metabolism
- PMID: 27216279
- PMCID: PMC4955733
- DOI: 10.1039/c6mb00175k
A clickable glutathione approach for identification of protein glutathionylation in response to glucose metabolism
Abstract
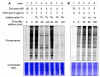
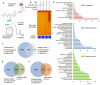
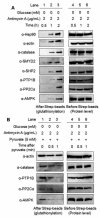
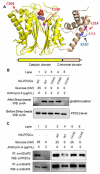
Glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function are closely interconnected with cellular redox-homeostasis. Although glucose starvation, which mimics ischemic conditions or insufficient vascularization, is known to perturb redox-homeostasis, global and individual protein glutathionylation in response to glucose metabolism or mitochondrial activity remains largely unknown. In this report, we use our clickable glutathione approach, which forms clickable glutathione (azido-glutathione) by using a mutant of glutathione synthetase (GS M4), for detection and identification of protein glutathionylation in response to glucose starvation. We found that protein glutathionylation is readily induced in HEK293 cells in response to low glucose concentrations when mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) are elevated in cells, and glucose is the major determinant for inducing reversible glutathionylation. Proteomic and biochemical analysis identified over 1300 proteins, including SMYD2, PP2Cα, and catalase. We further showed that PP2Cα is glutathionylated at C314 in a C-terminal domain, and PP2Cα C314 glutathionylation disrupts the interaction with mGluR3, an important glutamate receptor associated with synaptic plasticity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clickable Glutathione-Based Identification of Cysteine Glutathionylation.Curr Protoc. 2023 Oct;3(10):e907. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.907. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37818879 Free PMC article.
-
Clickable glutathione using tetrazine-alkene bioorthogonal chemistry for detecting protein glutathionylation.Org Biomol Chem. 2016 Nov 22;14(46):10886-10893. doi: 10.1039/c6ob02050j. Org Biomol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27812596
-
Metabolic synthesis of clickable glutathione for chemoselective detection of glutathionylation.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Aug 20;136(33):11566-9. doi: 10.1021/ja503946q. Epub 2014 Aug 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 25079194
-
Evaluating the Oxidative Stress in Renal Diseases: What Is the Role for S-Glutathionylation?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Jul 20;25(3):147-64. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6656. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26972776 Review.
-
S-glutathionylation, friend or foe in cardiovascular health and disease.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101693. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101693. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32912836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Defining the S-Glutathionylation Proteome by Biochemical and Mass Spectrometric Approaches.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;11(11):2272. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112272. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMYD2 glutathionylation contributes to degradation of sarcomeric proteins.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 18;9(1):4341. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06786-x. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30337525 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging chemistry and biology in protein glutathionylation.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Dec;71:102221. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102221. Epub 2022 Oct 9. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 36223700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary proteomic strategies for cysteine redoxome profiling.Plant Physiol. 2021 May 27;186(1):110-124. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaa074. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33793888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoproteomic strategy identified p120-catenin glutathionylation regulates E-cadherin degradation and cell migration.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Dec 21;30(12):1542-1556.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.004. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37714153 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

