Neuroprotective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal neurotoxicity
- PMID: 27162482
- PMCID: PMC4860370
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2016.20.3.279
Neuroprotective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal neurotoxicity
Abstract
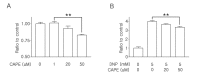
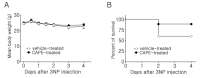
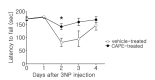
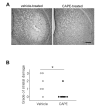
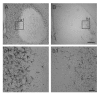
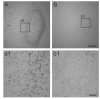
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), derived from honeybee hives, is a bioactive compound with strong antioxidant activity. This study was designed to test the neuroprotective effect of CAPE in 3-nitropropionic acid (3NP)-induced striatal neurotoxicity, a chemical model of Huntington's disease (HD). Initially, to test CAPE's antioxidant activity, a 2,2'-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) antioxidant assay was employed, and CAPE showed a strong direct radical-scavenging eff ect. In addition, CAPE provided protection from 3NP-induced neuronal cell death in cultured striatal neurons. Based on these observations, the in vivo therapeutic potential of CAPE in 3NP-induced HD was tested. For this purpose, male C57BL/6 mice were repeatedly given 3NP to induce HD-like pathogenesis, and 30 mg/kg of CAPE or vehicle (5% dimethyl sulfoxide and 95% peanut oil) was administered daily. CAPE did not cause changes in body weight, but it reduced mortality by 29%. In addition, compared to the vehicle-treated group, robustly reduced striatal damage was observed in the CAPE-treated animals, and the 3NP-induced behavioral defi cits on the rotarod test were signifi cantly rescued after the CAPE treatment. Furthermore, immunohistochemical data showed that immunoreactivity to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and CD45, markers for astrocyte and microglia activation, respectively, were strikingly reduced. Combined, these data unequivocally indicate that CAPE has a strong antioxidant eff ect and can be used as a potential therapeutic agent against HD.
Keywords: 3-nitropropionic acid; Antioxidant; Caff eic acid phenethyl ester; Huntington's disease; Striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclosporin A protects striatal neurons in vitro and in vivo from 3-nitropropionic acid toxicity.J Comp Neurol. 2000 Oct 2;425(4):471-8. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861(20001002)425:4<471::aid-cne1>3.0.co;2-u. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10975874
-
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) Prevents Development of STZ-ICV Induced dementia in Rats.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jan;13(Suppl 1):S10-S15. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.203974. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28479719 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester activation of Nrf2 pathway is enhanced under oxidative state: structural analysis and potential as a pathologically targeted therapeutic agent in treatment of colonic inflammation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:552-562. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23892357
-
The potential usage of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) against chemotherapy-induced and radiotherapy-induced toxicity.Cell Biochem Funct. 2012 Jul;30(5):438-43. doi: 10.1002/cbf.2817. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012. PMID: 22431158 Review.
-
3-Nitropropionic acid: a mitochondrial toxin to uncover physiopathological mechanisms underlying striatal degeneration in Huntington's disease.J Neurochem. 2005 Dec;95(6):1521-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03515.x. Epub 2005 Nov 21. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16300642 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Feb 14;2020:6565396. doi: 10.1155/2020/6565396. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32148547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;397(3):1791-1801. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02730-z. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37740773
-
Natural Phenolic Compounds with Neuroprotective Effects.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):306-326. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04046-z. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37940760 Review.
-
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) Protects PC12 Cells from Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity by Activating the NGF-Signaling Pathway.Neurotox Res. 2018 Jul;34(1):32-46. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9849-z. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29260495
-
The Neuroprotective Effects of Phenolic Acids: Molecular Mechanism of Action.Nutrients. 2017 May 10;9(5):477. doi: 10.3390/nu9050477. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28489058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gil JM, Rego AC. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2803–2820. - PubMed
-
- Semaka A, Creighton S, Warby S, Hayden MR. Predictive testing for Huntington disease: interpretation and significance of intermediate alleles. Clin Genet. 2006;70:283–294. - PubMed
-
- Sepers MD, Raymond LA. Mechanisms of synaptic dysfunction and excitotoxicity in Huntington's disease. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19:990–996. - PubMed
-
- Ueda M, Li S, Itoh M, Hayakawa-Yano Y, Wang MX, Hayakawa M, Hasebe-Matsubara R, Ohta K, Ohta E, Mizuno A, Hida Y, Matsumoto M, Chen H, Nakagawa T. Polyglutamine expansion disturbs the endoplasmic reticulum formation, leading to caspase-7 activation through Bax. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;443:1232–1238. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

