An Arntl2-Driven Secretome Enables Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastatic Self-Sufficiency
- PMID: 27150038
- PMCID: PMC4864124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.003
An Arntl2-Driven Secretome Enables Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastatic Self-Sufficiency
Abstract
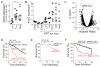
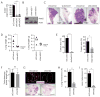
The ability of cancer cells to establish lethal metastatic lesions requires the survival and expansion of single cancer cells at distant sites. The factors controlling the clonal growth ability of individual cancer cells remain poorly understood. Here, we show that high expression of the transcription factor ARNTL2 predicts poor lung adenocarcinoma patient outcome. Arntl2 is required for metastatic ability in vivo and clonal growth in cell culture. Arntl2 drives metastatic self-sufficiency by orchestrating the expression of a complex pro-metastatic secretome. We identify Clock as an Arntl2 partner and functionally validate the matricellular protein Smoc2 as a pro-metastatic secreted factor. These findings shed light on the molecular mechanisms that enable single cancer cells to form allochthonous tumors in foreign tissue environments.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


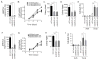
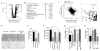


Similar articles
-
Upregulation of SOX9 in lung adenocarcinoma and its involvement in the regulation of cell growth and tumorigenicity.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Sep 1;16(17):4363-73. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0138. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20651055
-
MDA-9/Syntenin-Slug transcriptional complex promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion/metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):386-401. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6299. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26561205 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a human lung cancer cell line with high metastatic potential to multiple organs: gene expression associated with metastatic potential in human lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2012 Nov;28(5):1727-35. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1972. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22922681
-
Molecular definition of a metastatic lung cancer state reveals a targetable CD109-Janus kinase-Stat axis.Nat Med. 2017 Mar;23(3):291-300. doi: 10.1038/nm.4285. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28191885 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription repressor slug promotes carcinoma invasion and predicts outcome of patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Nov 15;11(22):8070-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0687. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16299238
Cited by
-
Identification and meta-analysis of copy number variation-driven circadian clock genes for colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4816-4824. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10830. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611992 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Nine-Gene Signature and Establishment of a Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Overall Survival of Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 27;9:996. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00996. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31612115 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Novel Prognostic Signature in Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Necroptosis-Related lncRNAs.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 22;13:833362. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.833362. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35938013 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1.Cell. 2019 Jul 11;178(2):316-329.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31257023 Free PMC article.
-
The Circadian Rhythm Gene Arntl2 Is a Metastasis Susceptibility Gene for Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer.PLoS Genet. 2016 Sep 22;12(9):e1006267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006267. eCollection 2016 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27656887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bafico A, Liu G, Goldin L, Harris V, Aaronson SA. An autocrine mechanism for constitutive Wnt pathway activation in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:497–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

