Electroresponsive Nanoparticles Improve Antiseizure Effect of Phenytoin in Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
- PMID: 27137202
- PMCID: PMC4965401
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-016-0431-9
Electroresponsive Nanoparticles Improve Antiseizure Effect of Phenytoin in Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Abstract
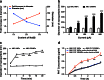
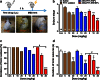
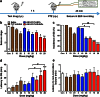
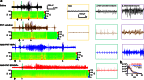
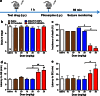
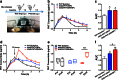
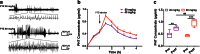
Previously, we developed electroresponsive hydrogel nanoparticles (ERHNPs) modified with angiopep-2 (ANG) to facilitate the delivery of the antiseizure drug phenytoin sodium (PHT). However, the electroresponsive characteristics were not verified directly in epileptic mice and the optimal preparation formula for electroresponsive ability is still unclear. Here, we further synthesized PHT-loaded ANG-ERHNPs (ANG-PHT-HNPs) and PHT-loaded nonelectroresponsive hydrogel nanoparticles (ANG-PHT-HNPs) by changing the content of sodium 4-vinylbenzene sulfonate in the preparation formulae. In vivo microdialysis analysis showed that ANG-PHT-ERHNPs not only have the characteristics of a higher distribution in the central nervous system, but also have electroresponsive ability, which resulted in a strong release of nonprotein-bound PHT during seizures. In both electrical- (maximal electrical shock) and chemical-induced (pentylenetetrazole and pilocarpine) seizure models, ANG-PHT-ERHNPs lowered the effective therapeutic doses of PHT and demonstrated the improved antiseizure effects compared with ANG-PHT-HNPs or PHT solution. These results demonstrate that ANG-ERHNPs are able to transport PHT into the brain efficiently and release them when epileptiform activity occurred, which is due to the content of sodium 4-vinylbenzene sulfonate in formula. This may change the therapeutic paradigm of existing drug treatment for epilepsy into a type of on-demand control for epilepsy in the future.
Keywords: Electroresponsive; Epilepsy; Microdialysis; Nanoparticle; Sodium 4-vinylbenzene sulfonate.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the online version of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiopep-conjugated electro-responsive hydrogel nanoparticles: therapeutic potential for epilepsy.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Nov 10;53(46):12436-40. doi: 10.1002/anie.201403846. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 25044856
-
Intranasal delivery of phenytoin-loaded nanoparticles to the brain suppresses pentylenetetrazol-induced generalized tonic clonic seizures in an epilepsy mouse model.Biomater Sci. 2021 Nov 9;9(22):7547-7564. doi: 10.1039/d1bm01251g. Biomater Sci. 2021. PMID: 34652351
-
Pluronic P85-coated poly(butylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles overcome phenytoin resistance in P-glycoprotein overexpressing rats with lithium-pilocarpine-induced chronic temporal lobe epilepsy.Biomaterials. 2016 Aug;97:110-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27162079
-
Phenytoin versus valproate monotherapy for partial onset seizures and generalised onset tonic-clonic seizures: an individual participant data review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 28;4(4):CD001769. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001769.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 09;8:CD001769. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001769.pub4. PMID: 27123830 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
Phenytoin versus valproate monotherapy for partial onset seizures and generalised onset tonic-clonic seizures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 23;(8):CD001769. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001769.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 28;4:CD001769. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001769.pub3. PMID: 23970302 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Cross-Linked Gels as Vehicles for Drug Delivery to Treat Central Nervous System Disorders.Gels. 2022 Sep 6;8(9):563. doi: 10.3390/gels8090563. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36135275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The blood-brain barrier: structure, regulation, and drug delivery.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 25;8(1):217. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01481-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37231000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical applications of stimuli-responsive nanomaterials.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 20;5(8):e643. doi: 10.1002/mco2.643. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39036340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GluN2B-Trp373 NMDA Receptor Variant is Associated with Autism-, Epilepsy-Related Phenotypes and Reduces NMDA Receptor Currents in Rats.Neurochem Res. 2022 Jun;47(6):1588-1597. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03554-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35181828
-
Antiepileptic drug-loaded and multifunctional iron oxide@silica@gelatin nanoparticles for acid-triggered drug delivery.Sci Rep. 2024 May 18;14(1):11400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62248-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38762571 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

