A Dynamical Framework for the All-or-None G1/S Transition
- PMID: 27136687
- PMCID: PMC4802413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.01.001
A Dynamical Framework for the All-or-None G1/S Transition
Abstract
The transition from G1 into DNA replication (S phase) is an emergent behavior resulting from dynamic and complex interactions between cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), Cdk inhibitors (CKIs), and the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). Understanding the cellular decision to commit to S phase requires a quantitative description of these interactions. We apply quantitative imaging of single human cells to track the expression of G1/S regulators and use these data to parametrize a stochastic mathematical model of the G1/S transition. We show that a rapid, proteolytic, double-negative feedback loop between Cdk2:Cyclin and the Cdk inhibitor p27(Kip1) drives a switch-like entry into S phase. Furthermore, our model predicts that increasing Emi1 levels throughout S phase are critical in maintaining irreversibility of the G1/S transition, which we validate using Emi1 knockdown and live imaging of G1/S reporters. This work provides insight into the general design principles of the signaling networks governing the temporally abrupt transitions between cell-cycle phases.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
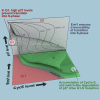
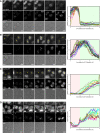
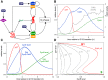
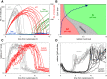
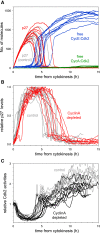
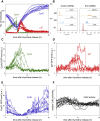
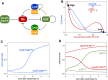
Comment in
-
Unraveling Cell-Cycle Dynamics in Cancer.Cell Syst. 2016 Jan 27;2(1):8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Cell Syst. 2016. PMID: 27136683
Similar articles
-
EMI1 switches from being a substrate to an inhibitor of APC/CCDH1 to start the cell cycle.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7709):313-317. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0199-7. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29875408 Free PMC article.
-
The anaphase-promoting complex works together with the SCF complex for proteolysis of the S-phase cyclin Clb6 during the transition from G1 to S phase.Fungal Genet Biol. 2016 Jun;91:6-19. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2016.03.004. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Fungal Genet Biol. 2016. PMID: 26994663
-
A conserved cyclin-binding domain determines functional interplay between anaphase-promoting complex-Cdh1 and cyclin A-Cdk2 during cell cycle progression.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;21(11):3692-703. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.11.3692-3703.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11340163 Free PMC article.
-
Control of the G1/S transition.Cancer Surv. 1997;29:7-23. Cancer Surv. 1997. PMID: 9338094 Review.
-
Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of vertebrate G1- and S-phase regulators.J Cell Physiol. 2001 Apr;187(1):1-10. doi: 10.1002/1097-4652(2001)9999:9999<1::AID-JCP1049>3.0.CO;2-O. J Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11241344 Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible APC(Cdh1) Inactivation Underlies the Point of No Return for Cell-Cycle Entry.Cell. 2016 Jun 30;166(1):167-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.077. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27368103 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative model of eukaryotic Cdk control through the Forkhead CONTROLLER.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2021 Jun 11;7(1):28. doi: 10.1038/s41540-021-00187-5. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 34117265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commentary: locating the restriction point.Cell Div. 2023 Feb 10;18(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13008-023-00085-8. Cell Div. 2023. PMID: 36765359 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive model for the proliferation-quiescence decision in response to endogenous DNA damage in human cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 6;115(10):2532-2537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715345115. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29463760 Free PMC article.
-
Intricate Regulatory Mechanisms of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome and Its Role in Chromatin Regulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 24;9:687515. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.687515. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34109183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bashir T., Dorrello N.V., Amador V., Guardavaccaro D., Pagano M. Control of the SCF(Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase by the APC/C(Cdh1) ubiquitin ligase. Nature. 2004;428:190–193. - PubMed
-
- Butz K., Shahabeddin L., Geisen C., Spitkovsky D., Ullmann A., Hoppe-Seyler F. Functional p53 protein in human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells. Oncogene. 1995;10:927–936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

