Different effects of arginine vasopressin on high-mobility group box 1 expression in astrocytes isolated from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats and congenic SHRpch1_18 rats
- PMID: 27126918
- PMCID: PMC4926054
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12172
Different effects of arginine vasopressin on high-mobility group box 1 expression in astrocytes isolated from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats and congenic SHRpch1_18 rats
Abstract
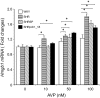
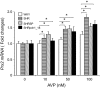
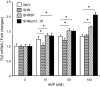
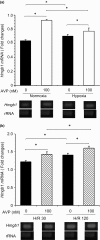
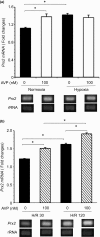
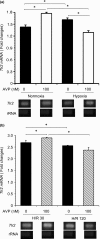
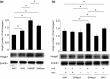
Stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSP/Izm) develop severe hypertension and astrocytic oedema following ischaemic stimulation. During ischaemic stress high-mobility group box 1 (Hmgb1) expression in astrocytes is induced, and subsequently potentiates deterioration of the brain due to ischaemic injury, which manifests as both cerebral inflammation and astrocytic oedema. Arginine vasopressin (AVP) induces brain injury and increases astrocytic swelling. After stroke, Hmgb1 and peroxiredoxin (Prx) are released at different times and activate macrophages in the brain via Toll-like receptors (Tlr2s). The purpose of this study was to examine whether AVP and/or hypoxia and reoxygenation (H/R) contribute to Hmgb1 regulation following ischaemic stroke. Thus, Hmgb1, Prx2 and Tlr2 expression levels in astrocytes isolated from Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY/Izm), spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR/Izm), SHRSP/Izm and congenic rat strain SHRpch1_18 treated with AVP and/or H/R were compared. Gene and protein expression levels were determined by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time quantitative PCR, and Western blot. mRNA expression of Hmgb1, Prx2 and Tlr2 induced by AVP was dose-dependent, and Hmgb1 and Prx2 expression was higher in SHR/Izm, SHRSP/Izm and SHRch1_18 than in WKY/Izm. Tlr2 expression with AVP was reduced in SHR/Izm compared to WKY/Izm. In SHRpch1_18, Hmgb1 expression increased after AVP plus H/R. AVP-modulated expression of Hmgb1 protein was reduced by the addition of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). These results suggest that oxidative stress by AVP enhanced expression of Hmgb1, Prx2 and Tlr2 in astrocytes. We hypothesize that regulation of Hmgb1 by AVP during H/R might be related to induction of inflammation and stroke in SHRSP/Izm and SHRpch1_18 rats.
Keywords: HMGB1; SHRSP; astrocytes.
© 2016 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2016 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures
References
-
- Borysiewicz E., Fil D. & Konat G.W. (2009) Rho proteins are negative regulators of TLR2, TLR3, and TLR4 signaling in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 87, 1565–1572. - PubMed
-
- Caso J.R., Pradillo J.M., Hurtado O., Leza J.C., Moro M.A. & Lizasoain I. (2008) Toll‐like receptor 4 is involved in subacute stress‐induced neuroinflammation and in the worsening of experimental stroke. Stroke 39, 1314–1320. - PubMed
-
- Faraco G., Fossati S., Bianchi M.E. et al (2007) High mobility group box 1 protein is released by neural cells upon different stresses and worsens ischemic neurodegeneration in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem. 103, 590–603. - PubMed
-
- Gandolgor T.A., Ohara H., Cui Z.H. et al (2013) Two genomic regions of chromosomes 1 and 18 explain most of the stroke susceptibility under salt loading in stroke‐prone spontaneously hypertensive rat/Izm. Hypertension 62, 55–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

