Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 27116120
- PMCID: PMC4946723
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12957
Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
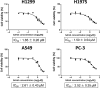
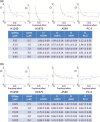
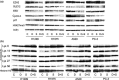
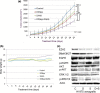
Recent discoveries have revealed that human cancer involves aberrant epigenetic alterations. We and others have previously shown that the histone methyltransferase EZH2, the catalytic subunit of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), is frequently overexpressed in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and that an EZH2 inhibitor, 3-deazaneplanocin A, inhibits the proliferation of NSCLC cells. Transcriptional silencing by EZH2 was recently shown to be required for the activity of histone deacetylases (HDACs) that interact with another PRC2 protein, EED. To develop a more effective epigenetic therapy for NSCLC, we determined the effects of co-treatment with 3-deazaneplanocin A and the HDAC inhibitor vorinostat (SAHA) in NSCLC cells. The co-treatment synergistically suppressed the proliferation of all tested NSCLC cell lines, regardless of their epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status. The synergistic effect was associated with slightly decreased histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation, modestly increased histone acetylation, and the depletion of EZH2 and other PRC2 proteins. The co-treatment resulted in an accumulation of p27Kip1, decrease in cyclin A, and increased apoptotic fraction in an additive/synergistic manner. Interestingly, the co-treatment strongly suppressed EGFR signaling, not only in EGFR-wild-type NSCLC cells, but also in EGFR-mutant cells, mainly through dephosphorylation of EGFR. Furthermore, the co-treatment suppressed the in vivo tumor growth of EGFR-mutant, EGFR-tyrosine kinase-resistant H1975 cells more effectively than did each agent alone, without visible toxicity. These results suggest that the combined pharmacological targeting of EZH2 and HDACs may provide more effective epigenetic therapeutics for NSCLC.
Keywords: 3-Deazaneplanocin A; EZH2; lung cancer; polycomb-group protein; vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid).
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epigenetic therapy with 3-deazaneplanocin A, an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2012 Nov;78(2):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22925699 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 inhibitors reverse resistance to gefitinib in primary EGFR wild-type lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2020 Dec 4;20(1):1189. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07667-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33276757 Free PMC article.
-
Superior efficacy of a combined epigenetic therapy against human mantle cell lymphoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Nov 15;18(22):6227-38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0873. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22932665 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting histone deacetylases: development of vorinostat for the treatment of cancer.Epigenomics. 2010 Jun;2(3):457-65. doi: 10.2217/epi.10.20. Epigenomics. 2010. PMID: 22121904 Review.
-
Targeting EZH2 and PRC2 dependence as novel anticancer therapy.Exp Hematol. 2015 Aug;43(8):698-712. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 28. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 26027790 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the polycomb repressive complex-2 related proteins with novel combinational strategies for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 1;10(10):3267-3284. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33163269 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Synergize with Catalytic Inhibitors of EZH2 to Exhibit Antitumor Activity in Small Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary, Hypercalcemic Type.Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Dec;17(12):2767-2779. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0348. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 30232145 Free PMC article.
-
Long intergenic non‑coding RNA 00467 promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation, migration and invasion by binding with EZH2 and repressing HTRA3 expression.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):640-654. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10292. Epub 2019 May 23. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31180543 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical studies reveal that LSD1 inhibition results in tumor growth arrest in lung adenocarcinoma independently of driver mutations.Mol Oncol. 2018 Nov;12(11):1965-1979. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12382. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30220105 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog pathway orchestrates the interplay of histone modifications and tailors combination epigenetic therapies in breast cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun;13(6):2601-2612. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.009. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37425067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 2380–8. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y et al Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11(2): 121–8. - PubMed
-
- Yano S, Wang W, Li Q et al Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor‐activating mutations. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9479–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

