The Ancient Evolutionary History of Polyomaviruses
- PMID: 27093155
- PMCID: PMC4836724
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005574
The Ancient Evolutionary History of Polyomaviruses
Abstract
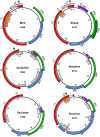
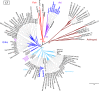
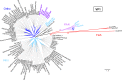
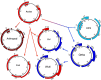
Polyomaviruses are a family of DNA tumor viruses that are known to infect mammals and birds. To investigate the deeper evolutionary history of the family, we used a combination of viral metagenomics, bioinformatics, and structural modeling approaches to identify and characterize polyomavirus sequences associated with fish and arthropods. Analyses drawing upon the divergent new sequences indicate that polyomaviruses have been gradually co-evolving with their animal hosts for at least half a billion years. Phylogenetic analyses of individual polyomavirus genes suggest that some modern polyomavirus species arose after ancient recombination events involving distantly related polyomavirus lineages. The improved evolutionary model provides a useful platform for developing a more accurate taxonomic classification system for the viral family Polyomaviridae.
Conflict of interest statement
AJM is an employee of Georgia Aquarium, Inc., a 501(c)3 not-for-profit organization. This affiliation does not alter our adherence to all PLOS Pathogens policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel lineage of polyomaviruses identified in bark scorpions.Virology. 2021 Nov;563:58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2021.08.008. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Virology. 2021. PMID: 34425496 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and molecular epidemiology of polyomaviruses.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Apr;79:104150. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.104150. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 31870972 Review.
-
Fish polyomaviruses belong to two distinct evolutionary lineages.J Gen Virol. 2018 Apr;99(4):567-573. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001041. Epub 2018 Mar 8. J Gen Virol. 2018. PMID: 29517483 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Polyomaviruses in Mammals from Multiple Orders and Reassessment of Polyomavirus Evolution and Taxonomy.Viruses. 2019 Oct 10;11(10):930. doi: 10.3390/v11100930. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31658738 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of the new human polyomaviruses.Rev Med Virol. 2012 Nov;22(6):354-77. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1711. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Rev Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 22461085 Review.
Cited by
-
Brincidofovir inhibits polyomavirus infection in vivo.mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0104924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01049-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38953354 Free PMC article.
-
Coinfections of Novel Polyomavirus, Anelloviruses and a Recombinant Strain of Myxoma Virus-MYXV-Tol Identified in Iberian Hares.Viruses. 2020 Mar 20;12(3):340. doi: 10.3390/v12030340. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32244962 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of genome simple sequence repeats signature in 98 Polyomaviridae species.3 Biotech. 2021 Jan;11(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02583-w. Epub 2021 Jan 6. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33432281 Free PMC article.
-
Serology Identifies LIPyV as a Feline Rather than a Human Polyomavirus.Viruses. 2023 Jul 13;15(7):1546. doi: 10.3390/v15071546. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515232 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse papillomaviruses identified in Weddell seals.J Gen Virol. 2018 Apr;99(4):549-557. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001028. Epub 2018 Feb 22. J Gen Virol. 2018. PMID: 29469687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gross L. A filterable agent, recovered from Ak leukemic extracts, causing salivary gland carcinomas in C3H mice. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, NY. 1953;83(2):414–21. . - PubMed
-
- Stewart SE, Eddy BE, Gochenour AM, Borgese NG, Grubbs GE. The induction of neoplasms with a substance released from mouse tumors by tissue culture. Virology. 1957;3(2):380–400. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

