Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway
- PMID: 27074917
- PMCID: PMC4867368
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00073-15
Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway
Abstract
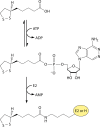
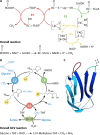
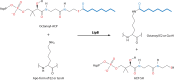
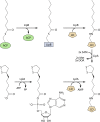
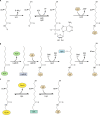
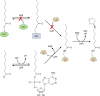
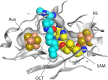
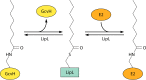
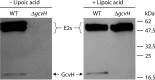
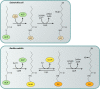
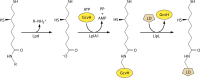
Although the structure of lipoic acid and its role in bacterial metabolism were clear over 50 years ago, it is only in the past decade that the pathways of biosynthesis of this universally conserved cofactor have become understood. Unlike most cofactors, lipoic acid must be covalently bound to its cognate enzyme proteins (the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases and the glycine cleavage system) in order to function in central metabolism. Indeed, the cofactor is assembled on its cognate proteins rather than being assembled and subsequently attached as in the typical pathway, like that of biotin attachment. The first lipoate biosynthetic pathway determined was that of Escherichia coli, which utilizes two enzymes to form the active lipoylated protein from a fatty acid biosynthetic intermediate. Recently, a more complex pathway requiring four proteins was discovered in Bacillus subtilis, which is probably an evolutionary relic. This pathway requires the H protein of the glycine cleavage system of single-carbon metabolism to form active (lipoyl) 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases. The bacterial pathways inform the lipoate pathways of eukaryotic organisms. Plants use the E. coli pathway, whereas mammals and fungi probably use the B. subtilis pathway. The lipoate metabolism enzymes (except those of sulfur insertion) are members of PFAM family PF03099 (the cofactor transferase family). Although these enzymes share some sequence similarity, they catalyze three markedly distinct enzyme reactions, making the usual assignment of function based on alignments prone to frequent mistaken annotations. This state of affairs has possibly clouded the interpretation of one of the disorders of human lipoate metabolism.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and retention of a primordial moonlighting pathway of protein modification in the absence of selection presents a puzzle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 23;115(4):647-655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718653115. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29339506 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of mature bovine H-protein of the glycine cleavage system in Escherichia coli and in vitro lipoylation of the apoform.J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20011-6. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1400316
-
Protein-protein interactions in assembly of lipoic acid on the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenases of aerobic metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):8263-8276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.194191. Epub 2011 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21209092 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. PMID: 24777537 Review.
-
Lipoate addition to acyltransferases of alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes and H-protein of glycine cleavage system.Methods Enzymol. 1997;279:184-93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(97)79022-0. Methods Enzymol. 1997. PMID: 9211270 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Recent progress of methods for cuproptosis detection.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Sep 4;11:1460987. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1460987. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39297074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional spectrum and specificity of mitochondrial ferredoxins FDX1 and FDX2.Nat Chem Biol. 2023 Feb;19(2):206-217. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-01159-4. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Nat Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 36280795 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Derived Cellular Models for Polytarget Precision Medicine in Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;16(10):1359. doi: 10.3390/ph16101359. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoate-binding proteins and specific lipoate-protein ligases in microbial sulfur oxidation reveal an atpyical role for an old cofactor.Elife. 2018 Jul 13;7:e37439. doi: 10.7554/eLife.37439. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30004385 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system to investigate lipoic acid metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 30;295(44):14973-14986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013760. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32843480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reed LJ. 1966. Chemistry and function of lipoic acid, p 99–126. In Florkin M, Stotz EH (ed), Comprehensive biochemistry, vol 14 Elsevier, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

