The cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin2 regulates brush border length and organization in Drosophila renal tubules
- PMID: 27072072
- PMCID: PMC4833865
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11266
The cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin2 regulates brush border length and organization in Drosophila renal tubules
Abstract
Multicellular organisms rely on cell adhesion molecules to coordinate cell-cell interactions, and to provide navigational cues during tissue formation. In Drosophila, Fasciclin 2 (Fas2) has been intensively studied due to its role in nervous system development and maintenance; yet, Fas2 is most abundantly expressed in the adult renal (Malpighian) tubule rather than in neuronal tissues. The role Fas2 serves in this epithelium is unknown. Here we show that Fas2 is essential to brush border maintenance in renal tubules of Drosophila. Fas2 is dynamically expressed during tubule morphogenesis, localizing to the brush border whenever the tissue is transport competent. Genetic manipulations of Fas2 expression levels impact on both microvilli length and organization, which in turn dramatically affect stimulated rates of fluid secretion by the tissue. Consequently, we demonstrate a radically different role for this well-known cell adhesion molecule, and propose that Fas2-mediated intermicrovillar homophilic adhesion complexes help stabilize the brush border.
Figures
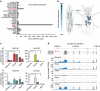
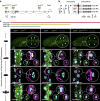
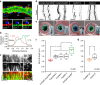
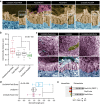

Similar articles
-
The Drosophila NCAM homolog Fas2 signals independently of adhesion.Development. 2020 Jan 22;147(2):dev181479. doi: 10.1242/dev.181479. Development. 2020. PMID: 31862845
-
In vivo induction of postsynaptic molecular assembly by the cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin2.J Cell Biol. 2007 Dec 17;179(6):1289-300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200705154. Epub 2007 Dec 10. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18070911 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins regulate DLG/FAS2 via a CaM kinase II-dependent pathway to mediate synapse elaboration and stabilization during postembryonic development.Development. 2002 Jul;129(14):3381-91. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.14.3381. Development. 2002. PMID: 12091308
-
[Genetic control of development of the Malpighian vessels in Drosophila melanogaster].Ontogenez. 2003 Sep-Oct;34(5):325-41. Ontogenez. 2003. PMID: 14582226 Review. Russian.
-
Renal tubule development in Drosophila: a closer look at the cellular level.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Feb;16(2):322-8. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004090729. Epub 2005 Jan 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 15647336 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules in epithelial morphogenesis: insights from Drosophila.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 12;375(1809):20190553. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0553. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32829687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized stellate cells offer a privileged route for rapid water flux in Drosophila renal tubule.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 21;117(3):1779-1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1915943117. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31907321 Free PMC article.
-
The septate junction protein Mesh is required for epithelial morphogenesis, ion transport, and paracellular permeability in the Drosophila Malpighian tubule.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):C675-C694. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00492.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31913700 Free PMC article.
-
Fasciclin 2 plays multiple roles in promoting cell migration within the developing nervous system of Manduca sexta.Dev Biol. 2023 Jul;499:31-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2023.04.009. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37121309 Free PMC article.
-
Basal microvilli define the metabolic capacity and lethal phenotype of pancreatic cancer.J Pathol. 2021 Mar;253(3):304-314. doi: 10.1002/path.5588. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33159698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chintapalli V. R., Wang J. & Dow J. A. T. Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 39, 715–720 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Grenningloh G., Jay Rehm E. & Goodman C. S. Genetic analysis of growth cone guidance in Drosophila: fasciclin II functions as a neuronal recognition molecule. Cell 67, 45–57 (1991). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

