Ablating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in CD11c+ cells perturbs intestinal epithelium development and intestinal immunity
- PMID: 27068235
- PMCID: PMC4828637
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23820
Ablating the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in CD11c+ cells perturbs intestinal epithelium development and intestinal immunity
Abstract
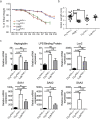
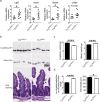
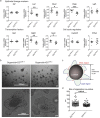
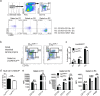
Diet and microbiome derived indole derivatives are known to activate the ligand induced transcription factor, the Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR). While the current understanding of AhR biology has confirmed its role in mucosal lymphocytes, its function in intestinal antigen presenting cells (APCs) is poorly understood. Here, we report that Cre-mediated deletion of AhR in CD11c-expressing cells in C57/BL6 mice is associated with altered intestinal epithelial morphogenesis in vivo. Moreover, when co-cultured with AhR-deficient DCs ex vivo, intestinal organoids showed reduced SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 and increased Mucin 2 expression, which correlates with reduced Paneth cells and increased goblet cell differentiation, similar to the data obtained in vivo. Further, characterization of intestinal APC subsets, devoid of AhR, revealed an expression pattern associated with aberrant intrinsic Wnt pathway regulation. At a functional level, the loss of AhR in APCs resulted in a dysfunctional epithelial barrier, associated with a more aggressive chemically induced colitis compared to wild type animals. Our results are consistent with a model whereby the AhR signalling pathway may participate in the regulation of innate immunity through intestinal epithelium development and mucosal immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through enhancing the differentiation of goblet cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jun 18;514(1):180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.136. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31029423
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor/microRNA-212/132 axis in T cells regulates IL-10 production to maintain intestinal homeostasis.Int Immunol. 2015 Aug;27(8):405-15. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv015. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Int Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25862525
-
Effects of high-fat diet and intestinal aryl hydrocarbon receptor deletion on colon carcinogenesis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G451-G463. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00268.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31905023 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and intestinal immunity.Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Jul;11(4):1024-1038. doi: 10.1038/s41385-018-0019-2. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Mucosal Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29626198 Review.
-
How Ah Receptor Ligand Specificity Became Important in Understanding Its Physiological Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9614. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249614. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Bacterial Metabolites on Gut Barrier Function and Host Immunity: A Focus on Bacterial Metabolism and Its Relevance for Intestinal Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 May 26;12:658354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658354. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34122415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intestinal microenvironment shapes macrophage and dendritic cell identity and function.Immunol Lett. 2023 Jan;253:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Immunol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36623708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of immunity by tryptophan microbial metabolites.Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 21;10:1209613. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1209613. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37521424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity and functions of intestinal mononuclear phagocytes.Mucosal Immunol. 2017 Jul;10(4):845-864. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.22. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Mucosal Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28378807 Review.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor and the gut-brain axis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Feb;18(2):259-268. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00585-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33408340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pocar P., Fischer B., Klonisch T. & Hombach-Klonisch S. Molecular interactions of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and its biological and toxicological relevance for reproduction. Reproduction 129, 379–389 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Bjeldanes L. F., Kim J. Y., Grose K. R., Bartholomew J. C. & Bradfield C. A. Aromatic hydrocarbon responsiveness-receptor agonists generated from indole-3-carbinol in vitro and in vivo: comparisons with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9543–9547 (1991). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zelante T. et al.. Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 39, 372–385 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Behnsen J. & Raffatellu M. Keeping the peace: aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling modulates the mucosal microbiota. Immunity 39, 206–207 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Moura-Alves P. et al.. AhR sensing of bacterial pigments regulates antibacterial defence. Nature 512, 387–392 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

