Neutrophils Contribute to the Protection Conferred by ArtinM against Intracellular Pathogens: A Study on Leishmania major
- PMID: 27058234
- PMCID: PMC4825989
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004609
Neutrophils Contribute to the Protection Conferred by ArtinM against Intracellular Pathogens: A Study on Leishmania major
Abstract
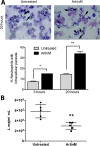
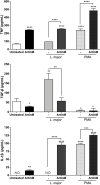
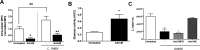
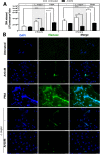
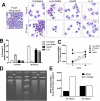
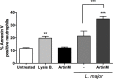
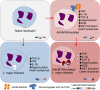
ArtinM, a D-mannose binding lectin from Artocarpus heterophyllus, has immunomodulatory activities through its interaction with N-glycans of immune cells, culminating with the establishment of T helper type 1 (Th1) immunity. This interaction protects mice against intracellular pathogens, including Leishmania major and Leishmania amazonensis. ArtinM induces neutrophils activation, which is known to account for both resistance to pathogens and host tissue injury. Although exacerbated inflammation was not observed in ArtinM-treated animals, assessment of neutrophil responses to ArtinM is required to envisage its possible application to design a novel immunomodulatory agent based on carbohydrate recognition. Herein, we focus on the mechanisms through which neutrophils contribute to ArtinM-induced protection against Leishmania, without exacerbating inflammation. For this purpose, human neutrophils treated with ArtinM and infected with Leishmania major were analyzed together with untreated and uninfected controls, based on their ability to eliminate the parasite, release cytokines, degranulate, produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), form neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and change life span. We demonstrate that ArtinM-stimulated neutrophils enhanced L. major clearance and at least duplicated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) release; otherwise, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) production was reduced by half. Furthermore, ROS production and cell degranulation were augmented. The life span of ArtinM-stimulated neutrophils decreased and they did not form NETs when infected with L. major. We postulate that the enhanced leishmanicidal ability of ArtinM-stimulated neutrophils is due to augmented release of inflammatory cytokines, ROS production, and cell degranulation, whereas host tissue integrity is favored by their shortened life span and the absence of NET formation. Our results reinforce the idea that ArtinM may be considered an appropriate molecular template for the construction of an efficient anti-infective agent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
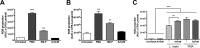
Similar articles
-
IL-17 Induction by ArtinM is Due to Stimulation of IL-23 and IL-1 Release and/or Interaction with CD3 in CD4+ T Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149721. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26901413 Free PMC article.
-
Lectins from Synadenium carinatum (ScLL) and Artocarpus heterophyllus (ArtinM) Are Able to Induce Beneficial Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model for Treatment of Toxoplasma gondii Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Nov 25;6:164. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00164. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27933277 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil activation induced by ArtinM: release of inflammatory mediators and enhancement of effector functions.Immunol Lett. 2009 Mar 24;123(1):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19428547
-
The immunomodulatory effect of plant lectins: a review with emphasis on ArtinM properties.Glycoconj J. 2013 Oct;30(7):641-57. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9464-4. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Glycoconj J. 2013. PMID: 23299509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH Oxidase Activation and Bacterial Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Aug 25;7:373. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00373. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28890882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adjuvant ArtinM favored the host immunity against Cryptococcus gattii infection in C57BL/6 mice.Immunotherapy. 2024;16(11):733-748. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2024.2360384. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Immunotherapy. 2024. PMID: 38940276
-
Effect of ArtinM on Human Blood Cells During Infection With Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 4;9:867. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00867. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29780375 Free PMC article.
-
The Modulation of NADPH Oxidase Activity in Human Neutrophils by Moroccan Strains of Leishmania major and Leishmania tropica Is Not Associated with p47phox Phosphorylation.Microorganisms. 2021 May 10;9(5):1025. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9051025. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34068760 Free PMC article.
-
ArtinM Cytotoxicity in B Cells Derived from Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Depends on Syk and Src Family Kinases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 5;24(2):1075. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021075. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674590 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of Human Neutrophils With Leishmania infantum or Leishmania major Strains Triggers Activation and Differential Cytokines Release.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 10;9:153. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00153. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31134162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robbins JB, Schneerson R, Szu SC (1995) Perspective: hypothesis: serum IgG antibody is sufficient to confer protection against infectious diseases by inactivating the inoculum. J Infect Dis 171: 1387–1398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

