Have Socioeconomic Inequalities in Tobacco Use in India Increased Over Time? Trends From the National Sample Surveys (2000-2012)
- PMID: 27048274
- PMCID: PMC4941603
- DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntw092
Have Socioeconomic Inequalities in Tobacco Use in India Increased Over Time? Trends From the National Sample Surveys (2000-2012)
Abstract
Introduction: India has experienced marked sociocultural change, economic growth and industry promotion of tobacco products over the past decade. Little is known about the influence of these factors on socioeconomic patterning of tobacco use. This study examines trends in tobacco use by socioeconomic status (SES) in India between 2000 and 2012.
Methods: We analyzed data in 2014 from nationally-representative repeated cross-sectional National Sample Surveys (NSS) in India for 1999-2000, 2004-2005 and 2011-2012 (n = 346 612 households). Prevalence and volume trends in cigarette, "bidi" and smokeless tobacco use were examined by household expenditure, educational attainment and caste/tribe status using Two-part model.
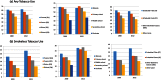
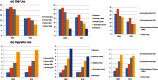
Results: Prevalence of any tobacco use remained consistent in the poorest households (61.5% to 62.7%) and declined among the richest (43.8% to 36.8%) between 2000-2012. Bidi use declined across all groups (poorest: 26.3% to 16.8%, richest: 19.8% to 10.7%) while cigarette use increased (poorest: 1.2% to 1.3%, richest: 6.5% to 7.0%). Relative to educated and general caste households, between 2000 and 2012 cigarette use in illiterate households increased by 38% and among Scheduled Tribe households increased by 32%. Smokeless tobacco use increased for all households (poorest: 26.2% to 33.9%, richest: 11.4% to 13.5%, Scheduled Tribe: 31.1% to 34.8%, general caste: 13.6% to 18.5%), with greater increases among richer, more educated and general caste households.
Conclusion: Marked SES patterning of tobacco use has persisted in India. Improving enforcement of tobacco control policies and monitoring comprehensive smoke-free legislations are needed to address this growing burden.
Implications: We found "resilient" tobacco patterns in the last decade despite prevention interventions. SES continues to be inversely associated with tobacco products, with the exception of cigarettes. The declines in bidi use may be getting replaced by increase in cigarette use trends, especially among lower SES groups. The use of smokeless tobacco products has increased across all SES groups and the volume of smokeless tobacco use is not been declining despite a number of policies on tobacco use. This may be attributed to inadequate attention to chewed forms of tobacco in current policies, particularly to implementing pictoral warnings and regulating surrogate advertising. Evaluating the implementation of anti-tobacco policies and ensuring equity dimensions in interventions is urgently needed to address tobacco use inequalities.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Socio-economic patterning of tobacco use in Indian states.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013 Aug;17(8):1110-7. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.12.0916. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013. PMID: 23827038 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in tobacco consumption in India 1987-2016: impact of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.Int J Public Health. 2019 Jul;64(6):841-851. doi: 10.1007/s00038-019-01252-x. Epub 2019 May 28. Int J Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31134319
-
Tobacco use, smoking quit rates, and socioeconomic patterning among men and women: a cross-sectional survey in rural Andhra Pradesh, India.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014 Oct;21(10):1308-18. doi: 10.1177/2047487313491356. Epub 2013 May 30. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 23723329
-
The Effect of Tobacco Control Policies on US Smokeless Tobacco Use: A Structured Review.Nicotine Tob Res. 2017 Dec 13;20(1):3-11. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntw291. Nicotine Tob Res. 2017. PMID: 27798090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determinants of smokeless tobacco use in India.Indian J Med Res. 2018 Jul;148(1):41-45. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_27_18. Indian J Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30264753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Socioeconomic patterning of chronic conditions and behavioral risk factors in rural South Asia: a multi-site cross-sectional study.Int J Public Health. 2017 Dec;62(9):1019-1028. doi: 10.1007/s00038-017-1019-9. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Int J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28756464
-
Impact of India's National Tobacco Control Programme on bidi and cigarette consumption: a difference-in-differences analysis.Tob Control. 2020 Jan;29(1):103-110. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054621. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Tob Control. 2020. PMID: 30554161 Free PMC article.
-
Uncontrolled hypertension among tobacco-users: women of prime childbearing age at risk in India.BMC Womens Health. 2021 Apr 9;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12905-021-01280-x. BMC Womens Health. 2021. PMID: 33836743 Free PMC article.
-
Possible role of nicotine and cotinine on nitroxidative stress and antioxidant content in saliva of smokeless tobacco consumers.Pract Lab Med. 2018 Jul 17;12:e00105. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2018.e00105. eCollection 2018 Nov. Pract Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 30090844 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns and related factors of bidi smoking in India.Tob Prev Cessat. 2020 May 4;6:28. doi: 10.18332/tpc/119053. eCollection 2020. Tob Prev Cessat. 2020. PMID: 32760863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eriksen M, Mackay J, Ross H. The Tobacco Atlas 2012. 4th ed. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2012. www.tobaccoatlas.org Accessed January 1, 2015.
-
- Srinath Reddy K, Shah B, Varghese C, Ramadoss A. Responding to the threat of chronic diseases in India. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1744–1749. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Reddy S, Ounpuu S, Anand S. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: Part II: variations in cardiovascular disease by specific ethnic groups and geographic regions and prevention strategies. Circulation. 2001;104(23):2855–2864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

