Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis by inducing host-derived indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase
- PMID: 27036118
- PMCID: PMC4818397
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-0979-0
Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis by inducing host-derived indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase
Abstract
Background: The immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) have prompted their therapeutic application in several autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis. Adult MSC are finite and their clinical use is restricted by the need for long-term expansion protocols that can lead to genomic instability. Inhibition of Smad2/3 signaling in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) provides an infinite source of MSC that match the phenotype and functional properties of adult MSC. Here, we test the therapeutic potential of hPSC-MSC of embryonic origin (embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells, hESC-MSC) in the experimental model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
Methods: CIA was induced in DBA/1 mice by immunization with type II collagen (CII) in Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA). Mice were treated with either a single dose (10(6) cells/mouse) of hESC-MSC on the day of immunization (prophylaxis) or with three doses of hESC-MSC every other day starting on the day of arthritis onset (therapy). Arthritis severity was evaluated daily for six weeks and ten days, respectively. Frequency of Treg (FoxP3(+)), Th1 (IFNγ(+)) and Th17 (IL17(+)) CD4(+) T cells in inguinal lymph nodes (ILN) was quantified by flow cytometry. Serum levels of anti-CII antibodies were determined by ELISA. Detection of hESC-MSC and quantification of murine and human indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO1) expression was performed by quantitative real-time PCR. Statistical differences were analyzed by ANOVA and the Mann-Whitney U test.
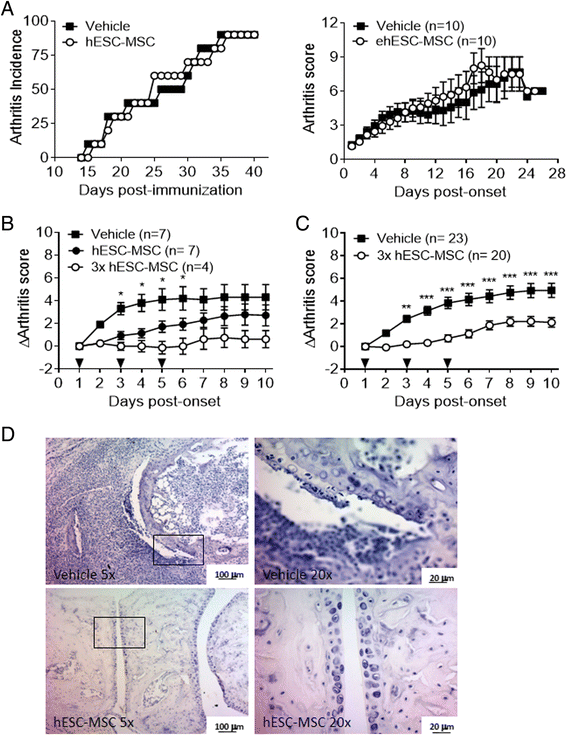
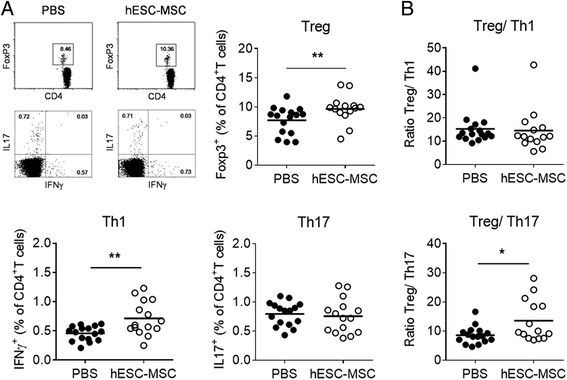
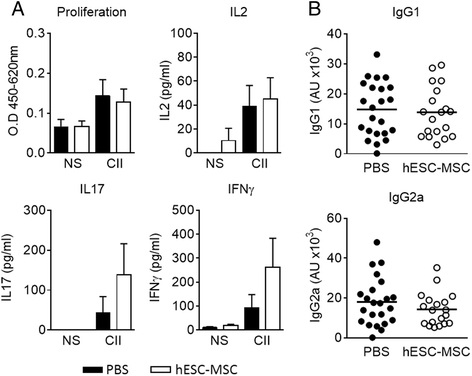
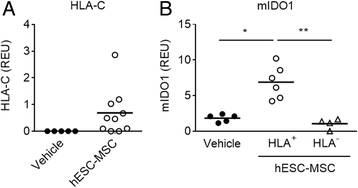
Results: Administration of hESC-MSC to mice with established arthritis reduced disease severity compared to control-treated mice. Analysis of CD4 T cell populations in treated mice showed an increase in FoxP3(+) Treg and IFNγ(+) Th1 cells but not in Th17 cells in the ILN. Anti-CII antibody levels were not affected by treatment. Migration of hESC-MSC to the ILN in treated mice was associated with the induction of murine IDO1.
Conclusion: Treatment with hESC-MSC ameliorates CIA by inducing IFNγ(+) Th1 cells and IDO1 in the host. Thus, hESC-MSC can provide an infinite cellular source for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Keywords: Arthritis; Cytokines; Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase; T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparable therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in collagen-induced arthritis to TNF inhibitor or anti-CD20 treatment.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017 Mar-Apr;35(2):288-295. Epub 2017 Jan 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28094754
-
Human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells suppress inflammation in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis and lung fibrosis by regulating T-cell function.Cytotherapy. 2024 Aug;26(8):930-938. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2024.03.008. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Cytotherapy. 2024. PMID: 38520411
-
Enhanced immunoregulation of mesenchymal stem cells by IL-10-producing type 1 regulatory T cells in collagen-induced arthritis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 1;6:26851. doi: 10.1038/srep26851. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27246365 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cell in experimental arthritis in rat and mouse models: A systematic review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Aug;46(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016. PMID: 27105756 Review.
-
Role of glycopeptide-specific T cells in collagen-induced arthritis: an example how post-translational modification of proteins may be involved in autoimmune disease.Ann Med. 2001 Oct;33(7):456-65. doi: 10.3109/07853890109002094. Ann Med. 2001. PMID: 11680793 Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Therapeutic Agents for the in vivo Treatment of Immune-Related Diseases: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 11;9:2056. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02056. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30254638 Free PMC article.
-
Application of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells in regenerative medicine.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Dec 26;13(12):1826-1844. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i12.1826. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 35069985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stability of housekeeping genes in inflamed joints of spontaneous and collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice.Inflamm Res. 2021 May;70(5):619-632. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01453-2. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33903928
-
Cell-based therapies for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Nov;11(11):e1091. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1091. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38018576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TSG-6 secreted by human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates severe acute pancreatitis via ER stress downregulation in mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Sep 26;9(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1009-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30257717 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

