Helical 1:1 α/Sulfono-γ-AA Heterogeneous Peptides with Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 27030636
- PMCID: PMC5340309
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00286
Helical 1:1 α/Sulfono-γ-AA Heterogeneous Peptides with Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
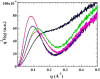
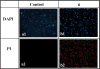
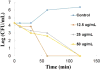
As one of the greatest threats facing the 21st century, antibiotic resistance is now a major public health concern. Host-defense peptides (HDPs) offer an alternative approach to combat emerging multi-drug-resistant bacteria. It is known that helical HDPs such as magainin 2 and its analogs adopt cationic amphipathic conformations upon interaction with bacterial membranes, leading to membrane disruption and subsequent bacterial cell death. We have previously shown that amphipathic sulfono-γ-AApeptides could mimic magainin 2 and exhibit bactericidal activity. In this article, we demonstrate for the first time that amphipathic helical 1:1 α/sulfono-γ-AA heterogeneous peptides, in which regular amino acids and sulfono-γ-AApeptide building blocks are alternatively present in a 1:1 pattern, display potent antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) suggests that the lead sequences adopt defined helical structures. The subsequent studies including fluorescence microscopy and time-kill experiments indicate that these hybrid peptides exert antimicrobial activity by mimicking the mechanism of HDPs. Our findings may lead to the development of HDP-mimicking antimicrobial peptidomimetics that combat drug-resistant bacterial pathogens. In addition, our results also demonstrate the effective design of a new class of helical foldamer, which could be employed to interrogate other important biological targets such as protein-protein interactions in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
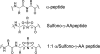


Similar articles
-
Helical Antimicrobial Sulfono-γ-AApeptides.J Med Chem. 2015 Jun 11;58(11):4802-11. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00537. Epub 2015 May 28. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26020456
-
Sulfono-γ-AApeptides as a new class of nonnatural helical foldamer.Chemistry. 2015 Feb 2;21(6):2501-7. doi: 10.1002/chem.201406112. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Chemistry. 2015. PMID: 25504756
-
Antibacterial activity of lipo-α/sulfono-γ-AA hybrid peptides.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 15;186:111901. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111901. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31771826 Free PMC article.
-
AApeptides as a new class of antimicrobial agents.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Jul 14;11(26):4283-90. doi: 10.1039/c3ob40444g. Epub 2013 May 31. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23722277 Review.
-
The development of antimicrobial γ-AApeptides.Future Med Chem. 2016 Jun;8(10):1101-10. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0034. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Future Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27284624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Development of Antimicrobial Peptidomimetics as Potential Drugs.Molecules. 2017 Aug 29;22(9):1430. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091430. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28850098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipidated α/α-AA heterogeneous peptides as antimicrobial agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jul 15;155:398-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29906686 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidated α/Sulfono-α-AA heterogeneous peptides as antimicrobial agents for MRSA.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Jan 1;28(1):115241. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115241. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31812324 Free PMC article.
-
Developments with investigating descriptors for antimicrobial AApeptides and their derivatives.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018 Aug;13(8):727-739. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1487950. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29933702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical approaches for exploring lipopeptide-lipid interactions.Biochimie. 2020 Mar;170:173-202. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.01.009. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 31978418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niu Y, Wang RE, Wu H, Cai J. Future Med Chem. 2012;4:1853–1862. - PubMed
-
- Marr AK, Gooderham WJ, Hancock REW. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:468–472. - PubMed
-
- Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
-
- Brown KL, Hancock REW. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Hancock REW, Sahl HG. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1551–1557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

