MicroRNA-122 regulates polyploidization in the murine liver
- PMID: 27016325
- PMCID: PMC4956491
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.28573
MicroRNA-122 regulates polyploidization in the murine liver
Abstract
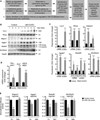
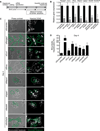
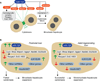
A defining feature of the mammalian liver is polyploidy, a numerical change in the entire complement of chromosomes. The first step of polyploidization involves cell division with failed cytokinesis. Although polyploidy is common, affecting ∼90% of hepatocytes in mice and 50% in humans, the specialized role played by polyploid cells in liver homeostasis and disease remains poorly understood. The goal of this study was to identify novel signals that regulate polyploidization, and we focused on microRNAs (miRNAs). First, to test whether miRNAs could regulate hepatic polyploidy, we examined livers from Dicer1 liver-specific knockout mice, which are devoid of mature miRNAs. Loss of miRNAs resulted in a 3-fold reduction in binucleate hepatocytes, indicating that miRNAs regulate polyploidization. Second, we surveyed age-dependent expression of miRNAs in wild-type mice and identified a subset of miRNAs, including miR-122, that is differentially expressed at 2-3 weeks, a period when extensive polyploidization occurs. Next, we examined Mir122 knockout mice and observed profound, lifelong depletion of polyploid hepatocytes, proving that miR-122 is required for complete hepatic polyploidization. Moreover, the polyploidy defect in Mir122 knockout mice was ameliorated by adenovirus-mediated overexpression of miR-122, underscoring the critical role miR-122 plays in polyploidization. Finally, we identified direct targets of miR-122 (Cux1, Rhoa, Iqgap1, Mapre1, Nedd4l, and Slc25a34) that regulate cytokinesis. Inhibition of each target induced cytokinesis failure and promoted hepatic binucleation.
Conclusion: Among the different signals that have been associated with hepatic polyploidy, miR-122 is the first liver-specific signal identified; our data demonstrate that miR-122 is both necessary and sufficient in liver polyploidization, and these studies will serve as the foundation for future work investigating miR-122 in liver maturation, homeostasis, and disease. (Hepatology 2016;64:599-615).
© 2016 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver physiological polyploidization: MicroRNA-122 a key regulator.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar;41(2):123-125. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.07.006. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28139382
-
TGFbeta Induces Binucleation/Polyploidization in Hepatocytes through a Src-Dependent Cytokinesis Failure.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 28;11(11):e0167158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167158. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27893804 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte polyploidization and its association with pathophysiological processes.Cell Death Dis. 2017 May 18;8(5):e2805. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.167. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28518148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incomplete cytokinesis/binucleation in mammals: The powerful system of hepatocytes.Methods Cell Biol. 2017;137:119-142. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 May 6. Methods Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28065301
-
Regulation of cytokinesis and its clinical significance.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015;52(4):159-67. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2015.1012191. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015. PMID: 26104038 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyploid Hepatocytes Facilitate Adaptation and Regeneration to Chronic Liver Injury.Am J Pathol. 2019 Jun;189(6):1241-1255. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30928253 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Extracellular RNA on Cell Behavior in Health, Disease and Regeneration.Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2017 Mar;5(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s40139-017-0121-2. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944104 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic And Epigenetic Regulation Of E-Cadherin Signaling In Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Oct 16;11:8947-8963. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S225606. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31802937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Polyploid State Restricts Hepatocyte Proliferation and Liver Regeneration in Mice.Hepatology. 2019 Mar;69(3):1242-1258. doi: 10.1002/hep.30286. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30244478 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct hepatocyte identities in liver homeostasis and regeneration.JHEP Rep. 2023 Apr 24;5(8):100779. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100779. eCollection 2023 Aug. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 37456678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guidotti JE, Bregerie O, Robert A, Debey P, Brechot C, Desdouets C. Liver cell polyploidization: a pivotal role for binuclear hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:19095–19101. - PubMed
-
- Margall-Ducos G, Celton-Morizur S, Couton D, Bregerie O, Desdouets C. Liver tetraploidization is controlled by a new process of incomplete cytokinesis. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:3633–3639. - PubMed
-
- Duncan AW. Aneuploidy, polyploidy and ploidy reversal in the liver. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013;24:347–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

