Corpora Amylacea of Brain Tissue from Neurodegenerative Diseases Are Stained with Specific Antifungal Antibodies
- PMID: 27013948
- PMCID: PMC4781869
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00086
Corpora Amylacea of Brain Tissue from Neurodegenerative Diseases Are Stained with Specific Antifungal Antibodies
Abstract
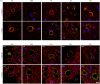
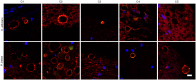
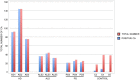
The origin and potential function of corpora amylacea (CA) remains largely unknown. Low numbers of CA are detected in the aging brain of normal individuals but they are abundant in the central nervous system of patients with neurodegenerative diseases. In the present study, we show that CA from patients diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease (AD) contain fungal proteins as detected by immunohistochemistry analyses. Accordingly, CA were labeled with different anti-fungal antibodies at the external surface, whereas the central portion composed of calcium salts contain less proteins. Detection of fungal proteins was achieved using a number of antibodies raised against different fungal species, which indicated cross-reactivity between the fungal proteins present in CA and the antibodies employed. Importantly, these antibodies do not immunoreact with cellular proteins. Additionally, CNS samples from patients diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Parkinson's disease (PD) also contained CA that were immunoreactive with a range of antifungal antibodies. However, CA were less abundant in ALS or PD patients as compared to CNS samples from AD. By contrast, CA from brain tissue of control subjects were almost devoid of fungal immunoreactivity. These observations are consistent with the concept that CA associate with fungal infections and may contribute to the elucidation of the origin of CA.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; corpora amylacea; fungal infection; neurodegenerative disease.
Figures
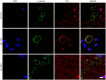
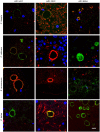
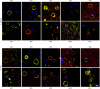
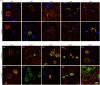
Similar articles
-
Human and Microbial Proteins From Corpora Amylacea of Alzheimer's Disease.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 29;8(1):9880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28231-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29959356 Free PMC article.
-
Immunochemical identification of ubiquitin and heat-shock proteins in corpora amylacea from normal aged and Alzheimer's disease brains.Acta Neuropathol. 1993;85(3):233-40. doi: 10.1007/BF00227716. Acta Neuropathol. 1993. PMID: 7681614
-
Fungal Enolase, β-Tubulin, and Chitin Are Detected in Brain Tissue from Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Front Microbiol. 2016 Nov 7;7:1772. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01772. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27872620 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Aug;97:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23756188 Review.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases: The immunological perspective.J Neuroimmunol. 2017 Dec 15;313:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Neuroimmunol. 2017. PMID: 29153601 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor 4 and CD11b expressed on microglia coordinate eradication of Candida albicans cerebral mycosis.Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113240. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113240. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37819761 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide, Identified Using an Antibody and by PAS Staining, Is Associated With Corpora amylacea and White Matter Injury in Alzheimer's Disease and Aging Brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 24;13:705594. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.705594. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899263 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin mediates the formation of corpora amylacea-like structures from degenerating neurons in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus after ischemia.Cell Tissue Res. 2022 Sep;389(3):443-463. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03645-6. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Cell Tissue Res. 2022. PMID: 35688947
-
Corpora amylacea are associated with tau burden and cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Aug 8;10(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01409-5. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35941704 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with specific detection of tau, TDP-43 and FUS pathology.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Jun 15;12(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01812-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38879502 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

