mTORC1-dependent translation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 drives neuroadaptations underlying excessive alcohol-drinking behaviors
- PMID: 26952865
- PMCID: PMC5097030
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2016.12
mTORC1-dependent translation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 drives neuroadaptations underlying excessive alcohol-drinking behaviors
Erratum in
-
mTORC1-dependent translation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 drives neuroadaptations underlying excessive alcohol-drinking behaviors.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Jan;23(1):164. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.252. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29133951 Free PMC article.
Abstract
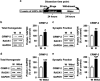
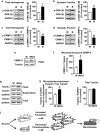
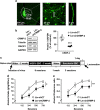
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) has an essential role in dendritic mRNA translation and participates in mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking and reconsolidation of alcohol-related memories. Here, we report that excessive alcohol consumption increases the translation of downstream targets of mTORC1, including collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP-2), in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) of rodents. We show that alcohol-mediated induction of CRMP-2 translation is mTORC1-dependent, leading to increased CRMP-2 protein levels. Furthermore, we demonstrate that alcohol intake also blocks glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β)-phosphorylation of CRMP-2, which results in elevated binding of CRMP-2 to microtubules and a concomitant increase in microtubule content. Finally, we show that systemic administration of the CRMP-2 inhibitor lacosamide, or knockdown of CRMP-2 in the NAc decreases excessive alcohol intake. These results suggest that CRMP-2 in the NAc is a convergent point that receives inputs from two signaling pathways, mTORC1 and GSK-3β, that in turn drives excessive alcohol-drinking behaviors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine D1 Receptor Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):701-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2254-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791202 Free PMC article.
-
GSK-3α/β-mediated phosphorylation of CRMP-2 regulates activity-dependent dendritic growth.J Neurochem. 2013 Jun;125(5):685-97. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12230. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23470087
-
GSK-3 mediates the okadaic acid-induced modification of collapsin response mediator protein-2 in human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Apr 15;103(6):1833-48. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21575. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17902168
-
[Molecular mechanisms of neuronal polarity].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2005 Aug;25(4):169-74. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2005. PMID: 16190365 Review. Japanese.
-
Molecular mechanisms of axon specification and neuronal disorders.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1086:116-25. doi: 10.1196/annals.1377.013. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17185510 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular tools to elucidate factors regulating alcohol use.Alcohol. 2019 Feb;74:3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30033149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol drinking exacerbates neural and behavioral pathology in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;148:169-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.10.017. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31733664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 increases operant alcohol self-administration in a manner associated with altered pGSK-3β, protein interacting with C kinase and GluA2 protein expression in the reward pathway of male C57BL/6J mice.Behav Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;31(1):15-26. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000501. Behav Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31503067 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ERK1/2 or CRMP2 Disrupts Alcohol Memory Reconsolidation and Prevents Relapse in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 17;25(10):5478. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105478. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791516 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta regulates ethanol consumption and is a risk factor for alcohol dependence.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Dec;43(13):2521-2531. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0202-x. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 30188517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ. Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 2006; 29: 565–598. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

