Foxl1-expressing mesenchymal cells constitute the intestinal stem cell niche
- PMID: 26949732
- PMCID: PMC4772878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.12.004
Foxl1-expressing mesenchymal cells constitute the intestinal stem cell niche
Abstract
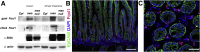
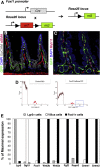
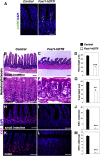
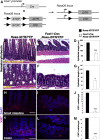
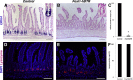
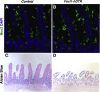
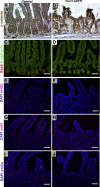
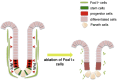
Background & aims: Intestinal epithelial stem cells that express Lgr5 and/or Bmi1 continuously replicate and generate differentiated cells throughout life1. Previously, Paneth cells were suggested to constitute an epithelium-intrinsic niche that regulates the behavior of these stem cells2. However, ablating Paneth cells has no effect on maintenance of functional stem cells3-5. Here, we demonstrate definitively that a small subset of mesenchymal, subepithelial cells expressing the winged-helix transcription factor Foxl1 are a critical component of the intestinal stem cell niche.
Methods: We genetically ablated Foxl1+ mesenchymal cells in adult mice using two separate models by expressing either the human or simian diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) under Foxl1 promoter control.
Conclusions: Killing Foxl1+ cells by diphtheria toxin administration led to an abrupt cessation of proliferation of both epithelial stem- and transit-amplifying progenitor-cell populations that was associated with a loss of active Wnt signaling to the intestinal epithelium. Therefore, Foxl1-expressing mesenchymal cells constitute the fundamental niche for intestinal stem cells.
Keywords: Intestinal stem cell niche; Wnt; mesenchyme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subepithelial telocytes are an important source of Wnts that supports intestinal crypts.Nature. 2018 May;557(7704):242-246. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0084-4. Epub 2018 May 2. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29720649 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone-induced expression of Foxl1 in subepithelial fibroblasts correlates with adult stem cell development during Xenopus intestinal remodeling.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 26;10(1):20715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77817-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33244068 Free PMC article.
-
The Intestinal Stem Cell Niche: A Central Role for Foxl1-Expressing Subepithelial Telocytes.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;8(1):111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30965141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foxl1-deficient mice exhibit aberrant epithelial cell positioning resulting from dysregulated EphB/EphrinB expression in the small intestine.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Jul;291(1):G163-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00019.2006. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16469829
-
Stromal control of intestinal development and the stem cell niche.Differentiation. 2019 Jul-Aug;108:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Differentiation. 2019. PMID: 30683451 Review.
Cited by
-
Consensus tissue domain detection in spatial omics data using multiplex image labeling with regional morphology (MILWRM).Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 30;7(1):1295. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06281-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39478141 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of intestinal epithelial homeostasis by mesenchymal cells.Inflamm Regen. 2024 Sep 26;44(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s41232-024-00355-0. Inflamm Regen. 2024. PMID: 39327633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Therapeutic Target for ALI/ARDS: Forkhead Box Transcription Factors.Lung. 2024 Oct;202(5):513-522. doi: 10.1007/s00408-024-00740-z. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Lung. 2024. PMID: 39259274 Review.
-
Cell competition in primary and metastatic colorectal cancer.Oncogenesis. 2024 Jul 26;13(1):28. doi: 10.1038/s41389-024-00530-5. Oncogenesis. 2024. PMID: 39060237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of FOXD1 in various cancers: a meta and bioinformation analysis.Future Sci OA. 2024 May 15;10(1):FSO901. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2023-0085. eCollection 2024. Future Sci OA. 2024. PMID: 38827805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barker N., van Es J.H., Kuipers J. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
