Novel methods for microCT-based analyses of vasculature in the renal cortex reveal a loss of perfusable arterioles and glomeruli in eNOS-/- mice
- PMID: 26936597
- PMCID: PMC4776352
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-016-0235-5
Novel methods for microCT-based analyses of vasculature in the renal cortex reveal a loss of perfusable arterioles and glomeruli in eNOS-/- mice
Abstract
Background: Two-dimensional measures of vascular architecture provide incomplete information about vascular structure. This study applied a novel rigorous method for 3D microCT-based analysis of total and cortical renal vasculature combined with a novel method to isolate and quantify the number of perfused glomeruli to assess vascular changes in eNOS-/- mice.
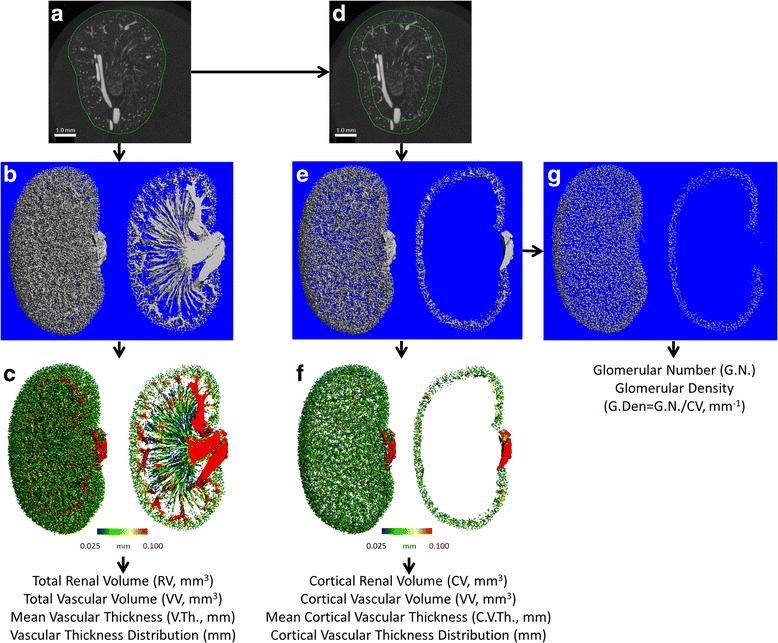
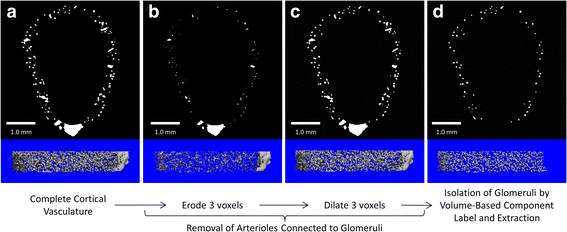
Methods: Two month old male wildtype and eNOS-/- mice were perfused with heparinized saline followed by radiopaque Microfil. The Microfil-perfused vasculature of excised kidneys was imaged by μCT with an isotropic voxel-size of 5.0 μm. For analysis of renal cortical vasculature, a custom algorithm was created to define the cortical volume of interest (VOI) as the entire volume within 600 μm of the renal surface. Vessel thickness in the whole kidney or renal cortex was analyzed by plotting the distribution of vascular volume at each measured thickness and examining differences between the genotypes at individual thicknesses. A second image processing algorithm was created to isolate, identify, and extract contrast perfused glomeruli from the cortical vessels.
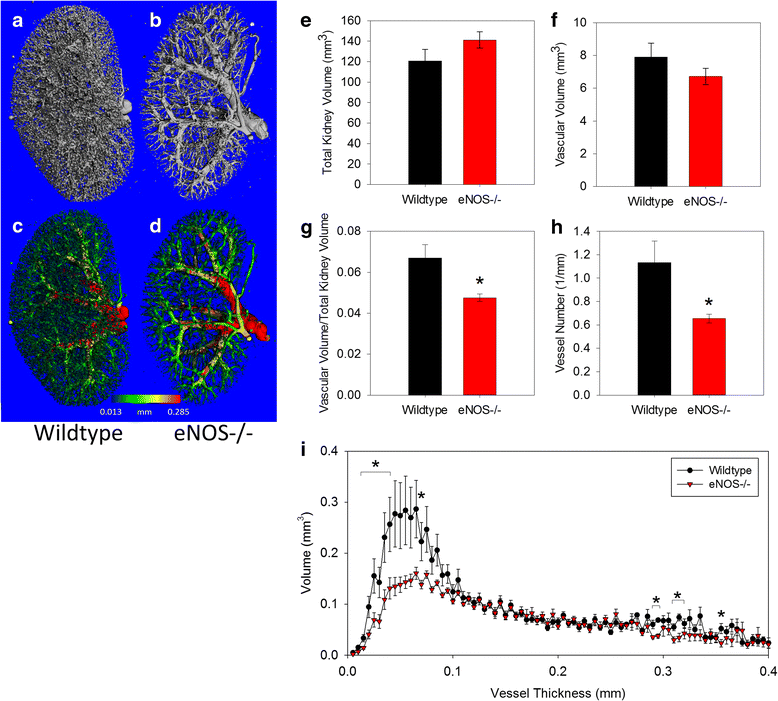
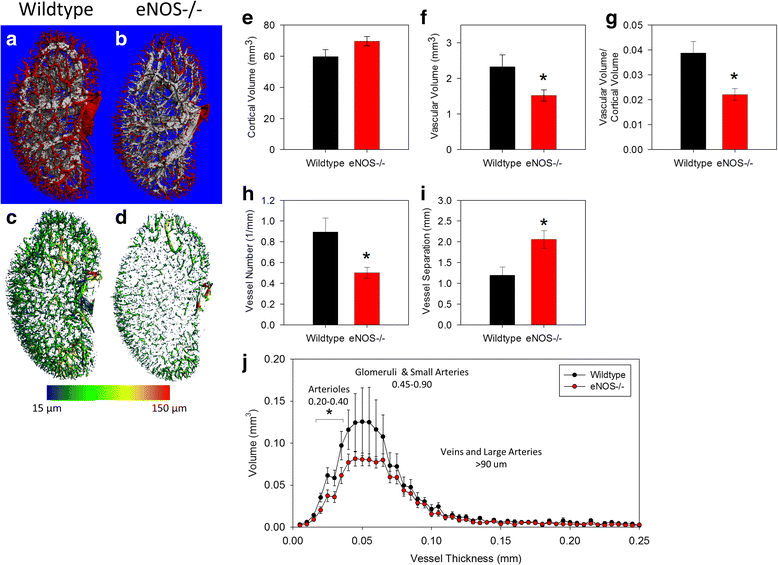
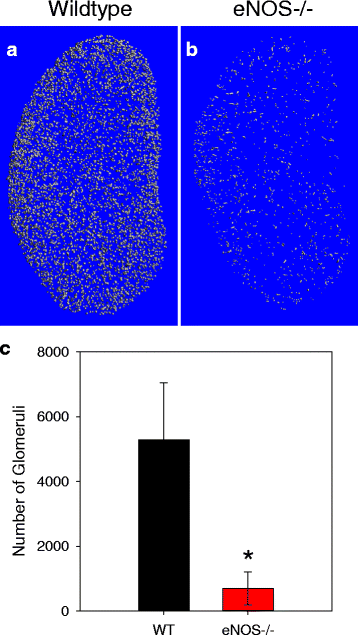
Results: Fractional vascular volume (vascular volume/kidney volume; VV/KV) and Vessel Number/mm (V.N) were significantly lower in eNOS-/- mice vs. WT (p < 0.05). eNOS-/- kidneys had significantly fewer perfusable vessels vs. WT in the range of 20-40 μm in thickness. The cortex of eNOS-/- kidneys had significantly lower VV, VV/cortical volume, and V.N, with an increase in the distance between vessels (all p < 0.05). The total volume of vessels in the range of 20-30 μm was significantly lower in the cortex of eNOS-/- mice compared to WT (p < 0.05). Moreover, the total number of perfused glomeruli was significantly decreased in eNOS-/- mice (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: The methods presented here demonstrate a new method to analyze contrast enhanced μCT images for vascular phenotyping of the murine kidney. These data also demonstrate that kidneys in eNOS-/- mice have severe defects in vascular perfusion/structure in the renal cortex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional microcomputed tomography of renal vasculature in rats.Hypertension. 1998 Jan;31(1 Pt 2):440-4. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.31.1.440. Hypertension. 1998. PMID: 9453342
-
The role of the RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling pathway in renal vascular reactivity in endothelial nitric oxide synthase null mice.J Hypertens. 2006 Jul;24(7):1429-36. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000234125.01638.3b. J Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16794494
-
Vascular architecture modifications in the steroid-induced polycystic kidney.Nephron. 1985;40(3):332-40. doi: 10.1159/000183488. Nephron. 1985. PMID: 4010848
-
Rapid non-genomic effects of aldosterone on the renal vasculature.Steroids. 2008 Oct;73(9-10):961-5. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.010. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Steroids. 2008. PMID: 18242654 Review.
-
[Micro-computed tomography of the vasculature in parenchymal organs and lung alveoli].Rofo. 2004 Sep;176(9):1219-25. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-813403. Rofo. 2004. PMID: 15346254 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Preclinical techniques to investigate exercise training in vascular pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):H1566-H1600. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00719.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33385323 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto a decellularized nerve allograft enhances angiogenesis in a rat sciatic nerve defect model.Microsurgery. 2020 Jul;40(5):585-592. doi: 10.1002/micr.30579. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Microsurgery. 2020. PMID: 32233045 Free PMC article.
-
Vessel network extraction and analysis of mouse pulmonary vasculature via X-ray micro-computed tomographic imaging.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Apr 20;17(4):e1008930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008930. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33878108 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Resolution Imaging with Ultrasound for Visualization of the Renal Microvasculature in Rats Before and After Renal Ischemia: A Pilot Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 22;10(11):862. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110862. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33105888 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Casting of Adult and Early Postnatal Mouse Lungs for Micro-CT Imaging.J Vis Exp. 2020 Jun 20;(160):10.3791/61242. doi: 10.3791/61242. J Vis Exp. 2020. PMID: 32628170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leelahavanichkul A, Yan Q, Hu X, Eisner C, Huang Y, Chen R, Mizel D, Zhou H, Wright EC, Kopp JB, et al. Angiotensin II overcomes strain-dependent resistance of rapid CKD progression in a new remnant kidney mouse model. Kidney Int. 2010;78(11):1136–1153. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

