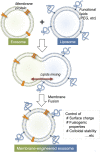
Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes
- PMID: 26911358
- PMCID: PMC4766490
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21933
Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes
Abstract
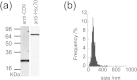
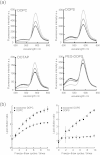
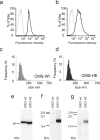
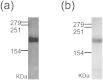
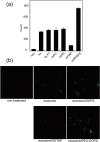
Exosomes are a valuable biomaterial for the development of novel nanocarriers as functionally advanced drug delivery systems. To control and modify the performance of exosomal nanocarriers, we developed hybrid exosomes by fusing their membranes with liposomes using the freeze-thaw method. Exosomes embedded with a specific membrane protein isolated from genetically modified cells were fused with various liposomes, confirming that membrane engineering methods can be combined with genetic modification techniques. Cellular uptake studies performed using the hybrid exosomes revealed that the interactions between the developed exosomes and cells could be modified by changing the lipid composition or the properties of the exogenous lipids. These results suggest that the membrane-engineering approach reported here offers a new strategy for developing rationally designed exosomes as hybrid nanocarriers for use in advanced drug delivery systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bioanalytical assay to distinguish cellular uptake routes for liposomes.Cytometry A. 2016 Mar;89(3):301-8. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22792. Epub 2015 Nov 9. Cytometry A. 2016. PMID: 26551759
-
Nanogel hybrid assembly for exosome intracellular delivery: effects on endocytosis and fusion by exosome surface polymer engineering.Biomater Sci. 2020 Jan 21;8(2):619-630. doi: 10.1039/c9bm01232j. Biomater Sci. 2020. PMID: 31833484
-
A method for screening mitochondrial fusogenic envelopes for use in mitochondrial drug delivery.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1141:57-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0363-4_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24567130
-
Single-Vesicle Assays Using Liposomes and Cell-Derived Vesicles: From Modeling Complex Membrane Processes to Synthetic Biology and Biomedical Applications.Chem Rev. 2018 Sep 26;118(18):8598-8654. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00777. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 30153012 Review.
-
Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Jun;38(6):754-763. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.12. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28392567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomembrane-Derived Nanoparticles in Alzheimer's Disease Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Synthetic Lipid Nanoparticles and Natural Cell-Derived Vesicles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 7;18:7441-7468. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S436774. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38090364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes for mRNA delivery: a novel biotherapeutic strategy with hurdles and hope.BMC Biotechnol. 2021 Mar 10;21(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12896-021-00683-w. BMC Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33691652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Liposomal Nanoplatinum for Targeted Cancer Chemophototherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 1;8(8):2003679. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003679. eCollection 2021 Apr. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 33898179 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in delivery systems for CRISPR/Cas-mediated cancer treatment: a focus on viral vectors and extracellular vesicles.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1444437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Based Hybrid Systems for Advanced Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 23;14(2):267. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020267. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valadi H. et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 654–659 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Properzi F., Logozzi M. & Fais S. Exosomes: the future of biomarkers in medicine. Biomark. Med. 7, 769–778 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Jia S. et al. Emerging technologies in extracellular vesicle-based molecular diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 14, 307–321 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

