Bioinspired Alkenyl Amino Alcohol Ionizable Lipid Materials for Highly Potent In Vivo mRNA Delivery
- PMID: 26889757
- PMCID: PMC5245883
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201505822
Bioinspired Alkenyl Amino Alcohol Ionizable Lipid Materials for Highly Potent In Vivo mRNA Delivery
Abstract
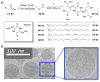
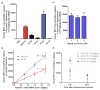
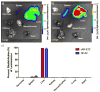
Thousands of human diseases could be treated by selectively controlling the expression of specific proteins in vivo. A new series of alkenyl amino alcohol (AAA) ionizable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) capable of delivering human mRNA with unprecedented levels of in vivo efficacy is demonstrated. This study highlights the importance of utilizing synthesis tools in tandem with biological inspiration to understand and improve nucleic acid delivery in vivo.
Keywords: RNA; biomaterials; drug delivery; nanoparticles; proteins.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Formulations for Therapeutic Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Dec 7;54(23):4283-4293. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00550. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34793124 Free PMC article.
-
Successful reprogramming of cellular protein production through mRNA delivered by functionalized lipid nanoparticles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 10;115(15):E3351-E3360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720542115. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29588418 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophobic scaffolds of pH-sensitive cationic lipids contribute to miscibility with phospholipids and improve the efficiency of delivering short interfering RNA by small-sized lipid nanoparticles.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jan 15;102:341-350. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.11.022. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31733331
-
Developing Biodegradable Lipid Nanoparticles for Intracellular mRNA Delivery and Genome Editing.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 2;54(21):4001-4011. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00500. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34668716 Review.
-
Chemical Design Strategy of Ionizable Lipids for In Vivo mRNA Delivery.ChemMedChem. 2024 Aug 19;19(16):e202400199. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400199. Epub 2024 Jun 25. ChemMedChem. 2024. PMID: 38722488 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomedicine for the Delivery of RNA in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 28;14(11):2677. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112677. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mechanism for the loss of mRNA activity in lipid nanoparticle delivery systems.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 22;12(1):6777. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26926-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34811367 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA-based modalities for infectious disease management.Nano Res. 2023;16(1):672-691. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4627-5. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Nano Res. 2023. PMID: 35818566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting materials and strategies for RNA delivery.Theranostics. 2023 Aug 21;13(13):4667-4693. doi: 10.7150/thno.87316. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37649616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-based Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jan 28;12(2):102. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020102. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32013049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sahin U, Kariko K, Tureci O. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:759–780. - PubMed
-
- Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:21–39. - PubMed
-
- Kormann MSD, Hasenpusch G, Aneja MK, Nica G, Flemmer AW, Herber-Jonat S, Huppmann M, Mays LE, Illenyi M, Schams A, Griese M, Bittmann I, Handgretinger R, Hartl D, Rosenecker J, Rudolph C. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:154–U196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

