Evaluation on the immunotherapy efficacies of synthetic peptide vaccines in asthmatic mice with group I and II allergens from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
- PMID: 26884956
- PMCID: PMC4723801
Evaluation on the immunotherapy efficacies of synthetic peptide vaccines in asthmatic mice with group I and II allergens from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Abstract
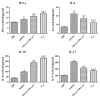
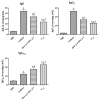
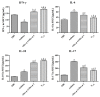
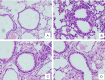
To assess the immunotherapy efficacies of recombinant vaccines containing T-cell epitopes derived from group I and allergens from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der p1, Der p2). Forty female BALB/c mice were randomized into groups of negative control (PBS group), positive controls (Asthma group), immunotherapy with rDer p1 and rDer p2 protein suspension (rDer p1/rDer p2 group) and specific immunotherapy with fusion peptide T1-8 (T1-8 group). Asthmatic mouse models were initially established with the crude extract from house dust mites (HDM), and PBS models were solely treated with PBS buffer. The two treatment groups were managed with corresponding protein via subcutaneous injection at the back 30 minutes before inhalation sensitization from day 25 to 27. Twenty-four hour following the final inhalation challenge, sera, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and the supernatant of splenocyte cultures (SSCC) were collected in each group of mice. ELISA was used to assay the levels of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10 and IL-17 in the BALF and SSCC, as well as serum levels of specific IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a. The lung tissue sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for pathological examination. ELISA detection revealed reduced levels of IL-4 and IL-17 in the BALF and SSCC, yet increased levels of IFN-γ and IL-10, and decreased specific serum IgE and IgG1, yet increased serum IgG2a in T1-8 group and rDer p1/rDer p2 group than asthma group (P<0.05). T1-8 group had lower IL-4 and IL-17 level and higher IFN-γ and IL-10 level in the BALF and SSCC as well as reduced specific serum IgE and IgG1, yet elevated IgG2a level compared to rDer p1/rDer p2 group (P<0.05). Examination on the lung sections indicated significantly abated pulmonary inflammation, less inflammatory cell infiltration and better remodeled airway epithelia in T1-8 group and rDer p1/rDer p2 group than asthma group. However, the airway epithelium structure T1-8 group and rDer p1/rDer p2 group remained similar to that of PBS group. In Conclusion, The recombinant protein T1-8, has effectively alleviated the allergic inflammation of airways and lungs in the experimental mice, suggesting that this synthetic peptide may be used as candidate vaccines for asthma on allergen-specific immunotherapy basis.
Keywords: Der p1; Der p2; Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; T cell epitope; specific immunotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A specific immune therapeutic effect of Der p2 T cell epitope vaccine on asthma mice].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 12;29(1):59-63. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2016120. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29469388 Chinese.
-
[Immunotherapy effect of ploypeptide vaccine of allergen group 1 from Dermatophagoides farinae on asthma mice].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;27(5):490-6. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26930933 Chinese.
-
[Effect of immunotherapy with recombinant allergen group 3 from dermatophagoides farinae in asthma mice].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;32(4):280-4. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25518591 Chinese.
-
[Experimental study on the Der f 1 mRNA molecules derived from dermatophagoides farinae for specific immunotherapy on murine model of asthma].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;32(4):268-73. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25518589 Chinese.
-
[Immunotherapeutic Effect of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus Group 1 Allergen T Cell Epitope Peptide Against Allergic Asthma in Mice].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;34(3):214-9. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 30129720 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Chinese Society of Allergy Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018 Jul;10(4):300-353. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.4.300. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29949830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D3 improves the effects of low dose Der p 2 allergoid treatment in Der p 2 sensitized BALB/c mice.Clin Mol Allergy. 2016 Aug 5;14:7. doi: 10.1186/s12948-016-0044-1. eCollection 2016. Clin Mol Allergy. 2016. PMID: 27499704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas WR, Hales BJ, Smith WA. House dust mite allergens in asthma and allergy. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergenspecific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:780–791. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Michel FB, Vignola AM. Allergen immunotherapy: therapeutic vaccines for asthma. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2004;18:511–528. - PubMed
-
- Durham SR, Walker SM, Varga EM, Jacobson MR, O’Brien F, Noble W, Till SJ, Hamid QA, Nouri-Aria KT. Long-term clinical efficacy of grass-pollen immunotherapy. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:468–475. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
