Glycomics and glycoproteomics of membrane proteins and cell-surface receptors: Present trends and future opportunities
- PMID: 26872045
- PMCID: PMC4889498
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201500552
Glycomics and glycoproteomics of membrane proteins and cell-surface receptors: Present trends and future opportunities
Abstract
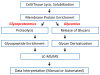
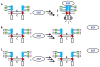
Membrane proteins mediate cell-cell interactions and adhesion, the transfer of ions and metabolites, and the transmission of signals from the extracellular environment to the cell interior. The extracellular domains of most cell membrane proteins are glycosylated, often at multiple sites. There is a growing awareness that glycosylation impacts the structure, interaction, and function of membrane proteins. The application of glycoproteomics and glycomics methods to membrane proteins has great potential. However, challenges also arise from the unique physical properties of membrane proteins. Successful analytical workflows must be developed and disseminated to advance functional glycoproteomics and glycomics studies of membrane proteins. This review explores the opportunities and challenges related to glycomic and glycoproteomic analysis of membrane proteins, including discussion of sample preparation, enrichment, and MS/MS analyses, with a focus on recent successful workflows for analysis of N- and O-linked glycosylation of mammalian membrane proteins.
Keywords: Glycomics; Glycopeptides; Glycoproteomics; Membrane proteins; Receptors.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Recent advances in glycopeptide enrichment and mass spectrometry data interpretation approaches for glycoproteomics analyses].Se Pu. 2021 Oct;39(10):1045-1054. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.06011. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34505426 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Current Technologies for Complex Glycoproteomics and Their Applications to Biology/Disease-Driven Glycoproteomics.J Proteome Res. 2018 Dec 7;17(12):4097-4112. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00515. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 30359034 Review.
-
Advances in LC-MS/MS-based glycoproteomics: getting closer to system-wide site-specific mapping of the N- and O-glycoproteome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1844(9):1437-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24830338 Review.
-
Towards structure-focused glycoproteomics.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Feb 26;49(1):161-186. doi: 10.1042/BST20200222. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 33439247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycomics-Assisted Glycoproteomics Enables Deep and Unbiased N-Glycoproteome Profiling of Complex Biological Specimens.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2628:235-263. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2978-9_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36781790
Cited by
-
Proteome Analysis of Serum Purified Using Solanum tuberosum and Lycopersicon esculentum Lectins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1315. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021315. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279312 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Modifications Controlling Membrane Raft Partitioning and Curvature in Human and Viral Proteins.J Phys Chem B. 2020 Sep 3;124(35):7574-7585. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c03435. Epub 2020 Aug 19. J Phys Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32813532 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric analysis of the N-glycoproteome in statin-treated liver cells with two lectin-independent chemical enrichment methods.Int J Mass Spectrom. 2018 Jun;429:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2017.05.010. Epub 2017 May 27. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2018. PMID: 30147434 Free PMC article.
-
The glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor ACE2.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Nov 15;6(1):396. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00809-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34782609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isotope-targeted glycoproteomics (IsoTaG) analysis of sialylated N- and O-glycopeptides on an Orbitrap Fusion Tribrid using azido and alkynyl sugars.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017 Jan;409(2):579-588. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9934-9. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017. PMID: 27695962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernandes H, Cohen S, Bishayee S. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(7):5375–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

