Genome-wide Analysis of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Integration and Strain in C666-1 and Raji Cells
- PMID: 26819646
- PMCID: PMC4716855
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.13150
Genome-wide Analysis of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Integration and Strain in C666-1 and Raji Cells
Abstract
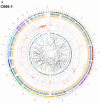
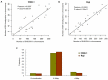
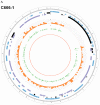
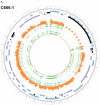
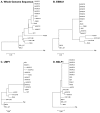
EBV is a key risk factor for many malignancy diseases such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and Burkitt lymphoma (BL). EBV integration has been reported, but its scale and impact to cancer development is remains unclear. C666-1 (NPC cell line) and Raji (BL cell line) are commonly studied EBV-positive cancer cells. A rare few EBV integration sites in Raji were found in previous research by traditional methods. To deeply survey EBV integration, we sequenced C666-1 and Raji whole genomes by the next generation sequencing (NGS) technology and a total of 909 breakpoints were detected in the two cell lines. Moreover, we observed that the number of integration sites was positive correlated with the total amount of chromosome structural variations (SVs) and copy number structural variations (CNVs), and most breakpoints located inside or nearby genome structural variations regions. It suggested that host genome instability provided an opportunity for EBV integration on one hand and the integration aggravated host genome instability on the other hand. Then, we respectively assembled the C666-1 and Raji EBV strains which would be useful resources for EBV-relative studies. Thus, we report the most comprehensive characterization of EBV integration in NPC cell and BL cell, and EBV shows the wide range and random integration to increase the tumorigenesis. The NGS provides an incomparable level of resolution on EBV integration and a convenient approach to obtain viral strain compared to any research technology before.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma (BL); C666-1; Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV); Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC); Raji; Whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Complete genomic sequence of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line C666-1.Infect Agent Cancer. 2013 Aug 2;8(1):29. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-8-29. Infect Agent Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23915735 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Epstein-Barr virus into chromosome 6q15 of Burkitt lymphoma cell line (Raji) induces loss of BACH2 expression.Am J Pathol. 2004 Mar;164(3):967-74. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63184-7. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 14982850 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Random Pattern of Integration for Epstein-Barr Virus with Preference for Gene-Poor Genomic Chromosomal Regions into the Genome of Burkitt Lymphoma Cell Lines.Viruses. 2022 Jan 4;14(1):86. doi: 10.3390/v14010086. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35062290 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic comparison of Epstein-Barr virus genomes.J Microbiol. 2018 Aug;56(8):525-533. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-8039-x. Epub 2018 Jun 14. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29948828 Review.
-
The biology and serology of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infections.Bull Cancer. 1976 Jul-Sep;63(3):399-410. Bull Cancer. 1976. PMID: 187269 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of exosomal non-coding RNAs in cancer metastasis.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 21;9(15):12487-12502. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23552. eCollection 2018 Feb 23. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29552328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OMSV enables accurate and comprehensive identification of large structural variations from nanochannel-based single-molecule optical maps.Genome Biol. 2017 Dec 1;18(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1356-2. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 29195502 Free PMC article.
-
Role of non-coding RNA in immune microenvironment and anticancer therapy of gastric cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Dec;100(12):1703-1719. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02264-6. Epub 2022 Nov 3. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36329206 Review.
-
Construction of a lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression Network for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:809760. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.809760. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875165 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is A Novel Biomarker in Various Cancers: A Meta-analysis Based on the GEO Database and Literature.J Cancer. 2016 May 20;7(8):991-1001. doi: 10.7150/jca.14663. eCollection 2016. J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27313790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meyer RM. EBV DNA: a Hodgkin lymphoma biomarker? Blood. 2013;121:3541–2. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Fan S, Zhang X. et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA 1 (EBER-1) could predict good prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Huang H, Huang L. et al. Regulation network and expression profiles of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs and their potential target host genes in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57:315–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

