FBXW7 Facilitates Nonhomologous End-Joining via K63-Linked Polyubiquitylation of XRCC4
- PMID: 26774286
- PMCID: PMC4744117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.010
FBXW7 Facilitates Nonhomologous End-Joining via K63-Linked Polyubiquitylation of XRCC4
Abstract
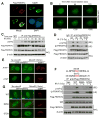
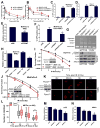
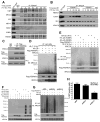
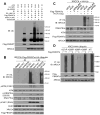
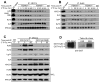
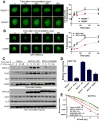
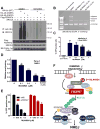
FBXW7 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor with loss-of-function mutations occurring in human cancers. FBXW7 inactivation causes genomic instability, but the mechanism remains elusive. Here we show that FBXW7 facilitates nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair and that FBXW7 depletion causes radiosensitization. In response to ionizing radiation, ATM phosphorylates FBXW7 at serine 26 to recruit it to DNA double-strand break (DSB) sites, whereas activated DNA-PKcs phosphorylates XRCC4 at serines 325/326, which promotes binding of XRCC4 to FBXW7. SCF(FBXW7) E3 ligase then promotes polyubiquitylation of XRCC4 at lysine 296 via lysine 63 linkage for enhanced association with the Ku70/80 complex to facilitate NHEJ repair. Consistent with these findings, a small-molecule inhibitor that abrogates XRCC4 polyubiquitylation reduces NHEJ repair. Our study demonstrates one mechanism by which FBXW7 contributes to genome integrity and implies that inactivated FBXW7 in human cancers could be a strategy for increasing the efficacy of radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The WD40 domain of FBXW7 is a poly(ADP-ribose)-binding domain that mediates the early DNA damage response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 7;47(8):4039-4053. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz058. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30722038 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interaction between DNA repair factors PAXX, XLF, XRCC4 and DNA-PKcs in human cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Jul;9(7):1315-1326. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12681. Epub 2019 Jun 12. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31141305 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase regulates DNA end resection in concert with Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) and ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM).J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37112-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514398. Epub 2013 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24220101 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PK: a dynamic enzyme in a versatile DSB repair pathway.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 May;17:21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.02.020. Epub 2014 Mar 27. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24680878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of FBXW7 in Gynecologic Malignancies.Cells. 2023 May 17;12(10):1415. doi: 10.3390/cells12101415. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of K63-linked ubiquitination in cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Oct 6;8(1):410. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01204-0. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 36202787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FBXW7-loss Sensitizes Cells to ATR Inhibition Through Induced Mitotic Catastrophe.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Dec 21;3(12):2596-2607. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0306. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 38032106 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-induced cell death increases the degradation of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex through the autophagy/lysosomal pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Feb;30(2):488-499. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01100-1. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36477079 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting neddylation modification alters mitochondrial morphology and reprograms energy metabolism in cancer cells.JCI Insight. 2019 Feb 21;4(4):e121582. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121582. eCollection 2019 Feb 21. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30668548 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis reveals driver cooperativity and novel mechanisms in endometrial carcinogenesis.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Oct 11;15(10):e17094. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202217094. Epub 2023 Aug 17. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37589076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, Cepeda D, Fiegl H, Dafou D, Marth C, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9006–9012. - PubMed
-
- Blank JL, Liu XJ, Cosmopoulos K, Bouck DC, Garcia K, Bernard H, Tayber O, Hather G, Liu R, Narayanan U, et al. Novel DNA Damage Checkpoints Mediating Cell Death Induced by the NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor MLN4924. Cancer Res. 2013;73:225–234. - PubMed
-
- Budman J, Chu G. Assays for nonhomologous end joining in extracts. Methods Enzymol. 2006;408:430–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

