The N-terminal Acetyltransferase Naa10/ARD1 Does Not Acetylate Lysine Residues
- PMID: 26755727
- PMCID: PMC4777859
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.709428
The N-terminal Acetyltransferase Naa10/ARD1 Does Not Acetylate Lysine Residues
Abstract
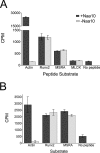
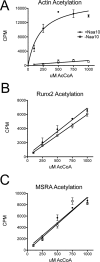
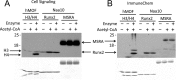
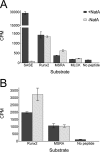
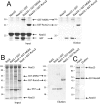
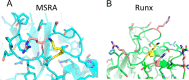
The N-terminal acetyltransferase NatA is a heterodimeric complex consisting of a catalytic subunit (Naa10/ARD1) and an auxiliary subunit (Naa15). NatA co-translationally acetylates the N termini of a wide variety of nascent polypeptides. In addition, Naa10 can act independently to posttranslationally acetylate a distinct set of substrates, notably actin. Recent structural studies of Naa10 have also revealed the molecular basis for N-terminal acetylation specificity. Surprisingly, recent reports claim that Naa10 may also acetylate lysine residues of diverse targets, including methionine sulfoxide reductase A, myosin light chain kinase, and Runt-related transcription factor 2. Here we used recombinant proteins to reconstitute and assess lysine acetylation events catalyzed by Naa10 in vitro. We show that there is no difference in lysine acetylation of substrate proteins with or without Naa10, suggesting that the substrates may be acetylated chemically rather than enzymatically. Together, our data argue against a role for Naa10 in lysine acetylation.
Keywords: ARD1; NAT; Naa10p; acetyl-CoA; acetylation; acetyltransferase; chemical acetylation; posttranslational modification (PTM); transcription factor.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
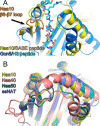
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Lysine Acetyltransferase Activity of Recombinant Human ARD1/NAA10.Molecules. 2020 Jan 29;25(3):588. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030588. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32013195 Free PMC article.
-
FIH permits NAA10 to catalyze the oxygen-dependent lysyl-acetylation of HIF-1α.Redox Biol. 2018 Oct;19:364-374. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30237125 Free PMC article.
-
Versatility of ARD1/NAA10-mediated protein lysine acetylation.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Jul 27;50(7):1-13. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0100-7. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30054464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the functionality of a ribosome-binding mutant of NAA15 using Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Jun 22;11(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3513-4. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29929531 Free PMC article.
-
The biological functions of Naa10 - From amino-terminal acetylation to human disease.Gene. 2015 Aug 10;567(2):103-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.085. Epub 2015 May 16. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25987439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The many lives of KATs - detectors, integrators and modulators of the cellular environment.Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Jan;20(1):7-23. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0072-4. Nat Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 30390049 Review.
-
Protein N-Terminal Acetylation: Structural Basis, Mechanism, Versatility, and Regulation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Jan;46(1):15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 32912665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic and genomic characterization of a yeast model for Ogden syndrome.Yeast. 2017 Jan;34(1):19-37. doi: 10.1002/yea.3211. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Yeast. 2017. PMID: 27668839 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Functions of the N-terminal Acetyltransferases Naa50 and NatA in Sister-chromatid Cohesion.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 2;291(36):19079-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.737585. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27422821 Free PMC article.
-
N-α-acetyltransferase 10 (NAA10) in development: the role of NAA10.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Jul 27;50(7):1-11. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0105-2. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30054454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verdin E., and Ott M. (2015) 50 years of protein acetylation: from gene regulation to epigenetics, metabolism and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 258–264 - PubMed
-
- Starheim K. K., Gevaert K., and Arnesen T. (2012) Protein N-terminal acetyltransferases: when the start matters. Trends Biochem. Sci. 37, 152–161 - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C., Kumar C., Gnad F., Nielsen M. L., Rehman M., Walther T. C., Olsen J. V., and Mann M. (2009) Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325, 834–840 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

