Structure of the hypusinylated eukaryotic translation factor eIF-5A bound to the ribosome
- PMID: 26715760
- PMCID: PMC4770232
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1517
Structure of the hypusinylated eukaryotic translation factor eIF-5A bound to the ribosome
Abstract
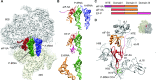
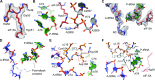
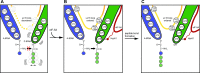
During protein synthesis, ribosomes become stalled on polyproline-containing sequences, unless they are rescued in archaea and eukaryotes by the initiation factor 5A (a/eIF-5A) and in bacteria by the homologous protein EF-P. While a structure of EF-P bound to the 70S ribosome exists, structural insight into eIF-5A on the 80S ribosome has been lacking. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of eIF-5A bound to the yeast 80S ribosome at 3.9 Å resolution. The structure reveals that the unique and functionally essential post-translational hypusine modification reaches toward the peptidyltransferase center of the ribosome, where the hypusine moiety contacts A76 of the CCA-end of the P-site tRNA. These findings would support a model whereby eIF-5A stimulates peptide bond formation on polyproline-stalled ribosomes by stabilizing and orienting the CCA-end of the P-tRNA, rather than by directly contributing to the catalysis.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural Basis for Polyproline-Mediated Ribosome Stalling and Rescue by the Translation Elongation Factor EF-P.Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 2;68(3):515-527.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.014. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 29100052
-
Crystal Structure of Hypusine-Containing Translation Factor eIF5A Bound to a Rotated Eukaryotic Ribosome.J Mol Biol. 2016 Sep 11;428(18):3570-3576. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 16. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27196944 Free PMC article.
-
Stall no more at polyproline stretches with the translation elongation factors EF-P and IF-5A.Mol Microbiol. 2016 Jan;99(2):219-35. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13233. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Mol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26416626 Review.
-
Hypusine: its post-translational formation in eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and its potential role in cellular regulation.Biofactors. 1993 May;4(2):95-104. Biofactors. 1993. PMID: 8347280 Review.
-
Crystal structure of elongation factor P from Thermus thermophilus HB8.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 29;101(26):9595-600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308667101. Epub 2004 Jun 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15210970 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
eIF5A is required for autophagy by mediating ATG3 translation.EMBO Rep. 2018 Jun;19(6):e46072. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846072. Epub 2018 Apr 30. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29712776 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into protein synthesis with proline residues.EMBO Rep. 2016 Dec;17(12):1776-1784. doi: 10.15252/embr.201642943. Epub 2016 Nov 8. EMBO Rep. 2016. PMID: 27827794 Free PMC article.
-
Nmd3 is a structural mimic of eIF5A, and activates the cpGTPase Lsg1 during 60S ribosome biogenesis.EMBO J. 2017 Apr 3;36(7):854-868. doi: 10.15252/embj.201696012. Epub 2017 Feb 8. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28179369 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the exportin Xpo4 in complex with RanGTP and the hypusine-containing translation factor eIF5A.Nat Commun. 2016 Jun 16;7:11952. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11952. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27306458 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of translation factor aIF5A from Sulfolobus solfataricus.Extremophiles. 2018 Sep;22(5):769-780. doi: 10.1007/s00792-018-1037-4. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Extremophiles. 2018. PMID: 30047030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ude S., Lassak J., Starosta A.L., Kraxenberger T., Wilson D.N., Jung K. Translation elongation factor EF-P alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches. Science. 2013;339:82–85. - PubMed
-
- Doerfel L.K., Wohlgemuth I., Kothe C., Peske F., Urlaub H., Rodnina M.V. EF-P is essential for rapid synthesis of proteins containing consecutive proline residues. Science. 2013;339:85–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

