The microRNA-29 Family Dictates the Balance Between Homeostatic and Pathological Glucose Handling in Diabetes and Obesity
- PMID: 26696639
- PMCID: PMC4876765
- DOI: 10.2337/db15-0770
The microRNA-29 Family Dictates the Balance Between Homeostatic and Pathological Glucose Handling in Diabetes and Obesity
Abstract
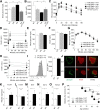
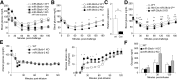
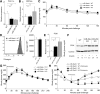
The microRNA-29 (miR-29) family is among the most abundantly expressed microRNA in the pancreas and liver. Here, we investigated the function of miR-29 in glucose regulation using miR-29a/b-1 (miR-29a)-deficient mice and newly generated miR-29b-2/c (miR-29c)-deficient mice. We observed multiple independent functions of the miR-29 family, which can be segregated into a hierarchical physiologic regulation of glucose handling. miR-29a, and not miR-29c, was observed to be a positive regulator of insulin secretion in vivo, with dysregulation of the exocytotic machinery sensitizing β-cells to overt diabetes after unfolded protein stress. By contrast, in the liver both miR-29a and miR-29c were important negative regulators of insulin signaling via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulation. Global or hepatic insufficiency of miR-29 potently inhibited obesity and prevented the onset of diet-induced insulin resistance. These results demonstrate strong regulatory functions for the miR-29 family in obesity and diabetes, culminating in a hierarchical and dose-dependent effect on premature lethality.
© 2016 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The microRNA-29 family: role in metabolism and metabolic disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):C367-C377. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00051.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35704699 Review.
-
MicroRNA-26a regulates insulin sensitivity and metabolism of glucose and lipids.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2497-509. doi: 10.1172/JCI75438. Epub 2015 May 11. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25961460 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hepatic miR-378 targets p110α and controls glucose and lipid homeostasis by modulating hepatic insulin signalling.Nat Commun. 2014 Dec 4;5:5684. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6684. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25471065
-
Identification of particular groups of microRNAs that positively or negatively impact on beta cell function in obese models of type 2 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2013 Oct;56(10):2203-12. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2993-y. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23842730
-
Influence of miRNA in insulin signaling pathway and insulin resistance: micro-molecules with a major role in type-2 diabetes.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):697-712. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1240. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24944010 Review.
Cited by
-
Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Inter-Organism, Cross-Species Communication and Drug Delivery.Proteomes. 2020 May 13;8(2):11. doi: 10.3390/proteomes8020011. Proteomes. 2020. PMID: 32414045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metazoan MicroRNAs.Cell. 2018 Mar 22;173(1):20-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.006. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29570994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulatory Role of MicroRNAs in Obesity and Obesity-Derived Ailments.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;14(11):2070. doi: 10.3390/genes14112070. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs, Parkinson's Disease, and Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 14;22(6):2953. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062953. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte expression of the micropeptide adropin regulates the liver fasting response and is enhanced by caloric restriction.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 2;295(40):13753-13768. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014381. Epub 2020 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32727846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choong CS, Priest JR, Foulkes WD. Exploring the endocrine manifestations of DICER1 mutations. Trends Mol Med 2012;18:503–505 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

