N-Terminus of Cardiac Myosin Essential Light Chain Modulates Myosin Step-Size
- PMID: 26671638
- PMCID: PMC4727542
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00817
N-Terminus of Cardiac Myosin Essential Light Chain Modulates Myosin Step-Size
Abstract
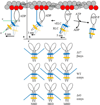
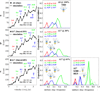
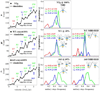
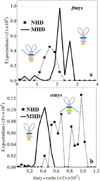
Muscle myosin cyclically hydrolyzes ATP to translate actin. Ventricular cardiac myosin (βmys) moves actin with three distinct unitary step-sizes resulting from its lever-arm rotation and with step-frequencies that are modulated in a myosin regulation mechanism. The lever-arm associated essential light chain (vELC) binds actin by its 43 residue N-terminal extension. Unitary steps were proposed to involve the vELC N-terminal extension with the 8 nm step engaging the vELC/actin bond facilitating an extra ∼19 degrees of lever-arm rotation while the predominant 5 nm step forgoes vELC/actin binding. A minor 3 nm step is the unlikely conversion of the completed 5 to the 8 nm step. This hypothesis was tested using a 17 residue N-terminal truncated vELC in porcine βmys (Δ17βmys) and a 43 residue N-terminal truncated human vELC expressed in transgenic mouse heart (Δ43αmys). Step-size and step-frequency were measured using the Qdot motility assay. Both Δ17βmys and Δ43αmys had significantly increased 5 nm step-frequency and coincident loss in the 8 nm step-frequency compared to native proteins suggesting the vELC/actin interaction drives step-size preference. Step-size and step-frequency probability densities depend on the relative fraction of truncated vELC and relate linearly to pure myosin species concentrations in a mixture containing native vELC homodimer, two truncated vELCs in the modified homodimer, and one native and one truncated vELC in the heterodimer. Step-size and step-frequency, measured for native homodimer and at two or more known relative fractions of truncated vELC, are surmised for each pure species by using a new analytical method.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro actin motility velocity varies linearly with the number of myosin impellers.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Mar 15;618:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28131772 Free PMC article.
-
Auxotonic to isometric contraction transitioning in a beating heart causes myosin step-size to down shift.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 19;12(4):e0174690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174690. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28423017 Free PMC article.
-
Ventricular myosin modifies in vitro step-size when phosphorylated.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jul;72:231-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.03.022. Epub 2014 Apr 12. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24726887 Free PMC article.
-
Fine tuning the myosin motor: the role of the essential light chain in striated muscle myosin.Biochimie. 2003 Jul;85(7):639-45. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(03)00131-7. Biochimie. 2003. PMID: 14505818 Review.
-
[Structure and function of the essential light chain of myosin].Biofizika. 2008 Nov-Dec;53(6):950-5. Biofizika. 2008. PMID: 19137676 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Natural variant frequencies across domains from different sarcomere proteins cross-correlate to identify inter-protein contacts associated with cardiac muscle function and disease.Mol Biomed. 2021 Nov 15;2(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s43556-021-00056-x. Mol Biomed. 2021. PMID: 35006463 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro actin motility velocity varies linearly with the number of myosin impellers.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Mar 15;618:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28131772 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin essential light chain 1sa decelerates actin and thin filament gliding on β-myosin molecules.J Gen Physiol. 2022 Oct 3;154(10):e202213149. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202213149. Epub 2022 Sep 2. J Gen Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36053243 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of myosin-binding protein H in thick filaments of developing vertebrate fast-twitch skeletal muscle.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 13:2024.05.10.593199. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.10.593199. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Gen Physiol. 2024 Dec 2;156(12):e202413604. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202413604. PMID: 38798399 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Hereditary heart disease: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and animal models of HCM, RCM, and DCM associated with mutations in cardiac myosin light chains.Pflugers Arch. 2019 May;471(5):683-699. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02257-4. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30706179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toepfer C, Caorsi V, Kampourakis T, Sikkel MB, West TG, Leung M-C, Al-Saud SA, MacLeod KT, Lyon AR, Marston SB, Sellers JR, Ferenczi MA. Myosin Regulatory Light Chain (RLC) Phosphorylation Change as a Modulator of Cardiac Muscle Contraction in Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:13446–13454. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

