Ulinastatin Protects against Acute Kidney Injury in Infant Piglets Model Undergoing Surgery on Hypothermic Low-Flow Cardiopulmonary Bypass
- PMID: 26656098
- PMCID: PMC4684368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144516
Ulinastatin Protects against Acute Kidney Injury in Infant Piglets Model Undergoing Surgery on Hypothermic Low-Flow Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Abstract
Objective: Infants are more vulnerable to kidney injuries induced by inflammatory response syndrome and ischemia-reperfusion injury following cardiopulmonary bypass especially with prolonged hypothermic low-flow (HLF). This study aims to evaluate the protective role of ulinastatin, an anti-inflammatory agent, against acute kidney injuries in infant piglets model undergoing surgery on HLF cardiopulmonary bypass.
Methods: Eighteen general-type infant piglets were randomly separated into the ulinastatin group (Group U, n = 6), the control group (Group C, n = 6), and the sham operation group (Group S, n = 6), and anaesthetized. The groups U and C received following experimental procedure: median thoracotomy, routine CPB and HLF, and finally weaned from CPB. The group S only underwent sham median thoracotomy. Ulinastatin at a dose of 5,000 units/kg body weight and a certain volume of saline were administrated to animals of the groups U and C at the beginning of CPB and at aortic declamping, respectively. Venous blood samples were collected at 3 different time points: after anesthesia induction in all experimental groups, 5 minutes, and 120 minutes after CPB in the Groups U and C. Markers for inflammation and acute kidney injury were tested in the collected plasma. N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) from urine, markers of oxidative stress injury and TUNEL-positive cells in kidney tissues were also detected.
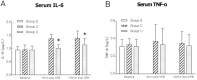
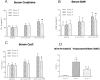
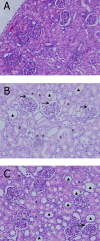
Results: The expressions of plasma inflammatory markers and acute kidney injury markers increased both in Group U and Group C at 5 min and 120 min after CPB. Also, numbers of TUNEL-positive cells and oxidative stress markers in kidney rose in both groups. At the time point of 120-min after CPB, compared with the Group C, some plasma inflammatory and acute kidney injury markers as well as TUNEL-positive cells and oxidative stress markers in kidney were significantly reduced in the Group U. Histologic analyses showed that HLF promoted acute tubular necrosis and dilatation.
Conclusions: HLF cardiopulmonary bypass surgery could intensify systemic inflammatory responses and oxidative stress on infant piglets, thus causing acute kidney injury. Ulinastatin might reduce such inflammatory response and oxidative stress and the extent of kidney injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ulinastatin as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory agent in infant piglets model undergoing surgery on hypothermic low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass.Paediatr Anaesth. 2013 Mar;23(3):209-16. doi: 10.1111/pan.12073. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013. PMID: 23384299
-
[Effects of alprostadil and ulinastatin on inflammatory response and lung injury after cardiopulmonary bypass in pediatric patients with congenital heart diseases].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Nov 11;88(41):2893-7. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 19080093 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Effects of ulinastatin on postoperative renal function after cardiopulmonary bypass].Masui. 1995 May;44(5):691-7. Masui. 1995. PMID: 7609298 Japanese.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass.Ann Vasc Surg. 2010 May;24(4):525-31. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20363104 Review.
-
Cardiopulmonary bypass associated acute kidney injury: better understanding and better prevention.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2331062. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2331062. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38515271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0.PLoS Biol. 2020 Jul 14;18(7):e3000411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663221 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrothermal extraction and physicochemical characterization of biogenic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles from buffalo waste bones for in vivo xenograft in experimental rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 15;13(1):17490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43989-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37840064 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaline Phosphatase Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury in an Infant Piglet Model of Cardiopulmonary Bypass with Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 2;9(1):14175. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50481-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31578351 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in inter-alpha inhibitor protein expression after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018 Apr;65:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29079121 Free PMC article.
-
Large animal models for translational research in acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):1042-1058. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1830108. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 33043785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pastuszko P, Schears GJ, Pirzadeh A, Kubin J, Greeley WJ, Wilson DF, et al. (2012) Effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on expression of selected proteins involved in regulation of apoptosis in the brain of newborn piglets after cardiopulmonary bypass and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 143:1436–1442. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.01.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Day JR, Taylor KM (2005) The systemic inflammatory response syndrome and cardiopulmonary bypass. Int J Surg 3:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Yin R, Shao H, Dong G, Luo L, Jing H (2007) N-acetylcysteine to ameliorate acute renal injury in a rat cardiopulmonary bypass model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 133:696–703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

