'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment
- PMID: 26641934
- PMCID: PMC4718764
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1979
'Deadman' and 'Passcode' microbial kill switches for bacterial containment
Abstract
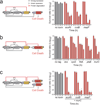
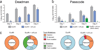
Biocontainment systems that couple environmental sensing with circuit-based control of cell viability could be used to prevent escape of genetically modified microbes into the environment. Here we present two engineered safeguard systems known as the 'Deadman' and 'Passcode' kill switches. The Deadman kill switch uses unbalanced reciprocal transcriptional repression to couple a specific input signal with cell survival. The Passcode kill switch uses a similar two-layered transcription design and incorporates hybrid LacI-GalR family transcription factors to provide diverse and complex environmental inputs to control circuit function. These synthetic gene circuits efficiently kill Escherichia coli and can be readily reprogrammed to change their environmental inputs, regulatory architecture and killing mechanism.
Figures
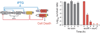

Comment in
-
Synthetic biology: Genetic kill switches--a matter of life or death.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Feb;17(2):67. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.29. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26688199 No abstract available.
-
Synthetic biology: Building genetic containment.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Feb;12(2):55-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2004. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26784843 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synthetic biology: Genetic kill switches--a matter of life or death.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Feb;17(2):67. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.29. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26688199 No abstract available.
-
[Bacterial containment system regulated by the concentration of salicylate].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2008 Feb;24(2):323-7. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18464620 Chinese.
-
Synthetic biology: Building genetic containment.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Feb;12(2):55-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2004. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26784843 No abstract available.
-
Plasmids as Tools for Containment.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0011-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104372 Review.
-
Suicide microbes on the loose.Biotechnology (N Y). 1995 Jan;13(1):35-7. doi: 10.1038/nbt0195-35. Biotechnology (N Y). 1995. PMID: 9634748 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Principles for designing synthetic microbial communities.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Jun;31:146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27084981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 3;13(1):672. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28163-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35115506 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding and Engineering Distributed Biochemical Pathways in Microbial Communities.Biochemistry. 2019 Jan 15;58(2):94-107. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01006. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30457843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Transcriptional Output of Synthetic Multi-input Promoters.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Aug 17;7(8):1834-1843. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00165. Epub 2018 Aug 1. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 30040895 Free PMC article.
-
Steering and controlling evolution - from bioengineering to fighting pathogens.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Dec;24(12):851-867. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00623-8. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 37400577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
METHODS ONLY-REFERENCES
-
- Larkin MA, et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–2948. - PubMed
-
- Bell CE, Lewis M. A closer view of the conformation of the Lac repressor bound to operator. Nature structural biology. 2000;7:209–214. - PubMed
-
- Friedman AM, Fischmann TO, Steitz TA. Crystal structure of lac repressor core tetramer and its implications for DNA looping. Science. 1995;268:1721–1727. - PubMed
-
- Lewis M, et al. Crystal structure of the lactose operon repressor and its complexes with DNA and inducer. Science. 1996;271:1247–1254. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher MA, Choi KY, Lu F, Zalkin H, Brennan RG. Mechanism of corepressor-mediated specific DNA binding by the purine repressor. Cell. 1995;83:147–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

