Prognostic significance of peripheral monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and monocytes in patients newly diagnosed with diffuse large b-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 26629001
- PMCID: PMC4658890
Prognostic significance of peripheral monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and monocytes in patients newly diagnosed with diffuse large b-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Objective: The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) aids in predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but R-IPI yields no significant differences in assessing different subtypes of DLBCL. It is necessary to identify patients with a high-risk of DLBCL and alternative therapy should be delivered as early as possible.
Methods: In total, 144 patients newly diagnosed with DLBCL including 63 GCB-DLBCL and 81 non-GCB-DLBCL and 30 healthy controls were enrolled. Peripheral monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSC) (CD14(+)HLA(-)DR(low/-)) were detected by flow cytometry and the percentage of monocytes (MΦ) was evaluated by completed blood count (CBC). The correlation between M-MDSC% and MΦ% was statistically analyzed.
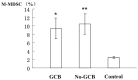
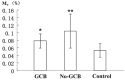
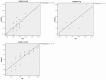
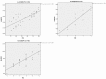
Results: Compared with healthy controls, significant increase was observed in M-MDSC% and MΦ% in DLBCL patients (both P<0.001). Significant difference of M-MDSC% was found between GCB-DLBCL and non-GCB-DLBCL patients in both poor (P<0.001) and very good groups (P=0.03), whereas no statistical significance in the good group (P>0.05). The MΦ% in non-GCB-DLBCL patients was significantly higher than that in GCB-DLBCL counterparts merely in the poor group (P<0.001). Positive correlation was noted between MΦ% and M-MDSC in all DLBCL patients rather than in healthy controls (r=0.227 P=0.229).
Conclusion: The percentage of peripheral MΦ was positively correlated with M-MDSC% in patients with different subtypes and risks of DLBCL. Peripheral MΦ% and M-MDSC% combined with R-IPI score may be useful for predicting the prognosis of patients newly-diagnosed with DLBCL.
Keywords: Monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; monocyte; revised international prognostic index.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and systemic inflammation in newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with chemoimmunotherapy.Exp Hematol. 2024 Jan;129:104125. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2023.10.004. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Exp Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38743005
-
[Prognostic Value of CD14+HLA-DRlow/- Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Jun;27(3):816-819. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2019.03.028. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31204937 Chinese.
-
T-cell defect in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas involves expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells.Blood. 2016 Aug 25;128(8):1081-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-08-662783. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27338100 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic Significance of Monocytes and Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(2):521-30. doi: 10.1159/000445644. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27383764
-
Treatment approach to newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Semin Hematol. 2015 Apr;52(2):107-18. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Semin Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25805590 Review.
Cited by
-
HLA-DR expression on monocytes and outcome of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for large B-cell lymphoma.Blood Adv. 2023 Mar 14;7(5):744-755. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006563. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 35439292 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells coming of age.Nat Immunol. 2018 Feb;19(2):108-119. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0022-x. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29348500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated M-MDSCs in Circulation Are Indicative of Poor Prognosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 19;10(8):1768. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081768. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33921711 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Secondary to Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: A New Therapeutic Targeting of Haematological Malignancies.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 28;10(9):1919. doi: 10.3390/jcm10091919. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33925214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells as immunological biomarkers in refractory/relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: translational results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002323. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002323. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34158317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Habermann T. New developments in the management of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematology. 2012;17(Suppl 1):S93–7. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Jaffe ES. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC; 2010. p. 233.
-
- Goldman LS, Andrew I. Goldman’s Cecil Medicine. 24th edition. 2012. p. 1222.
-
- Akyurek N, Uner A, Benekli M, Barista I. Prognostic significance of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 rearrangements in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone plus rituximab. Cancer. 2011;118:4173–4183. - PubMed
-
- Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Fermé C, Christian B, Lepage E, Tilly H, Morschhauser F, Gaulard P, Salles G, Bosly A, Gisselbrecht C, Reyes F, Coiffier B. Long-Term Results of the R-CHOP Study in the Treatment of Elderly Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study by the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:4117–4126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
