Endothelial LRP1 transports amyloid-β(1-42) across the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 26619118
- PMCID: PMC4701557
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI81108
Endothelial LRP1 transports amyloid-β(1-42) across the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
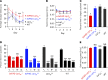
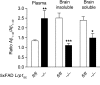
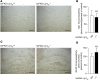
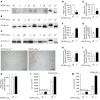
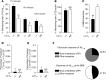
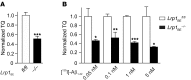
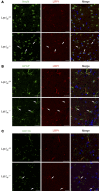
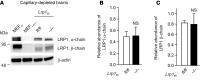
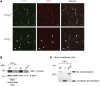
According to the neurovascular hypothesis, impairment of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) in brain capillaries of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) contributes to neurotoxic amyloid-β (Aβ) brain accumulation and drives Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. However, due to conflicting reports on the involvement of LRP1 in Aβ transport and the expression of LRP1 in brain endothelium, the role of LRP1 at the BBB is uncertain. As global Lrp1 deletion in mice is lethal, appropriate models to study the function of LRP1 are lacking. Moreover, the relevance of systemic Aβ clearance to AD pathology remains unclear, as no BBB-specific knockout models have been available. Here, we developed transgenic mouse strains that allow for tamoxifen-inducible deletion of Lrp1 specifically within brain endothelial cells (Slco1c1-CreER(T2) Lrp1(fl/fl) mice) and used these mice to accurately evaluate LRP1-mediated Aβ BBB clearance in vivo. Selective deletion of Lrp1 in the brain endothelium of C57BL/6 mice strongly reduced brain efflux of injected [125I] Aβ(1-42). Additionally, in the 5xFAD mouse model of AD, brain endothelial-specific Lrp1 deletion reduced plasma Aβ levels and elevated soluble brain Aβ, leading to aggravated spatial learning and memory deficits, thus emphasizing the importance of systemic Aβ elimination via the BBB. Together, our results suggest that receptor-mediated Aβ BBB clearance may be a potential target for treatment and prevention of Aβ brain accumulation in AD.
Figures
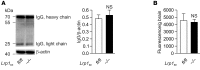
Similar articles
-
LRP1 mediates bidirectional transcytosis of amyloid-β across the blood-brain barrier.Neurobiol Aging. 2011 Dec;32(12):2323.e1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.025. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Neurobiol Aging. 2011. PMID: 20630619
-
Inhibition of ADAM10 promotes the clearance of Aβ across the BBB by reducing LRP1 ectodomain shedding.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016 Aug 8;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12987-016-0038-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016. PMID: 27503326 Free PMC article.
-
The concerted amyloid-beta clearance of LRP1 and ABCB1/P-gp across the blood-brain barrier is linked by PICALM.Brain Behav Immun. 2018 Oct;73:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2018. PMID: 30041013 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of lipoprotein receptors in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008 Feb;5(1):15-25. doi: 10.2174/156720508783884675. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008. PMID: 18288927 Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1: a serial clearance homeostatic mechanism controlling Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide elimination from the brain.J Neurochem. 2010 Dec;115(5):1077-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07002.x. Epub 2010 Oct 5. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20854368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Data-independent acquisition proteomic analysis of the brain microvasculature in Alzheimer's disease identifies major pathways of dysfunction and upregulation of cytoprotective responses.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Oct 21;21(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00581-1. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39434151 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Novel Therapeutics Targeting the Blood-Brain Barrier: From Barrier to Carrier.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Aug;8(16):e2101090. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101090. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34085418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasminogen Activators in Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 22;22(9):4380. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094380. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fundamental Role for Oxidants and Intracellular Calcium Signals in Alzheimer's Pathogenesis-And How a Comprehensive Antioxidant Strategy May Aid Prevention of This Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 21;22(4):2140. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042140. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age dependency of cerebral P-glycoprotein function in wild-type and APPPS1 mice measured with PET.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Jan;40(1):150-162. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18806640. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 30354871 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

