Therapeutic Actions of the Thiazolidinediones in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26587016
- PMCID: PMC4637502
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/957248
Therapeutic Actions of the Thiazolidinediones in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
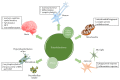
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial metabolic brain disorder characterized by protein aggregates, synaptic failure, and cognitive impairment. In the AD brain is common to observe the accumulation of senile plaques formed by amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide and the neurofibrillary tangles composed of modified tau protein, which both lead to cellular damage and progressive neurodegeneration. Currently, there is no effective therapy for AD; however several studies have shown that the treatments with the peroxisome proliferators activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ) agonists known as thiazolidinedione drugs (TZDs), like rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, attenuate neurodegeneration and improve cognition in mouse models and patients with mild-to-moderate AD. Furthermore, studies on animal models have shown that TZDs inhibit neuroinflammation, facilitate amyloid-β plaque clearance, enhance mitochondrial function, improve synaptic plasticity, and, more recently, attenuate tau hyperphosphorylation. How TZDs may improve or reduce these pathologic signs of AD and what the mechanisms and the implicated pathways in which these drugs work are are questions that remain to be answered. However, in this review, we will discuss several cellular targets, in which TZDs can be acting against the neurodegeneration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Disease modifying effect of chronic oral treatment with a neurotrophic peptidergic compound in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Nov;71:110-30. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 25046994
-
[Pathological changes induced by amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011 Jan;131(1):3-11. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.131.3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21212607 Review. Japanese.
-
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid-β in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019;16(5):418-452. doi: 10.2174/1567205016666190321163438. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019. PMID: 30907320 Review.
Cited by
-
A Dichotomous Role for FABP7 in Sleep and Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis: A Hypothesis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:798994. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.798994. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35844236 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Antidiabetic Agents as Therapeutic Approaches for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 6;15(9):e44763. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44763. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37809189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Effectiveness of GTM-1, Rapamycin, and Carbamazepine on Autophagy and Alzheimer Disease.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Feb 14;23:801-808. doi: 10.12659/msm.898679. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28193995 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone ameliorates Aβ42 deposition in rats with diet-induced insulin resistance associated with AKT/GSK3β activation.Mol Med Rep. 2017 May;15(5):2588-2594. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6342. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28447730 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of select cognitive domains with rosiglitazone implicates dorsal hippocampus circuitry sensitive to PPARγ agonism in an Alzheimer's mouse model.Brain Behav. 2021 Feb;11(2):e01973. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1973. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33382528 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

