Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 26579470
- PMCID: PMC4629442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.001
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
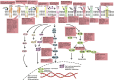
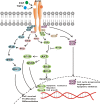
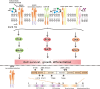
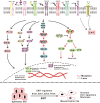
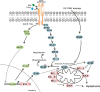
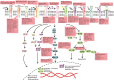
Since the discovery that non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is driven by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs, e.g., gefitinib and elrotinib) have been effectively used for clinical treatment. However, patients eventually develop drug resistance. Resistance to EGFR-TKIs is inevitable due to various mechanisms, such as the secondary mutation (T790M), activation of alternative pathways (c-Met, HGF, AXL), aberrance of the downstream pathways (K-RAS mutations, loss of PTEN), impairment of the EGFR-TKIs-mediated apoptosis pathway (BCL2-like 11/BIM deletion polymorphism), histologic transformation, ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter effusion, etc. Here we review and summarize the known resistant mechanisms to EGFR-TKIs and provide potential targets for development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: ABC, ATP binding cassette; ABCB1, ATP binding cassette, sub-family B, member 1; ABCC1, ATP binding cassette, sub-family C, member 1; ABCC10, ATP binding cassette, sub-family C, member 10; ABCG2, ATP binding cassette, sub-family G, member 2; AKT, protein kinase B; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; AXL, Anexelekto; BCL-2, B-cell CLL/lymphoma-2; BCL2L11/BIM, BCL2-like 11; BH3, BCL2-homology domain 3; BRAF, v-RAF murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1; CML, chronic myelogenous leukemia; CRKL, Crk-like protein; EGFR; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; EGFR-TKIs, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors; EGFRvIII, EGFR variant III; EML4, echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4; EMT, epithelial mesenchymal transition; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; FGFRs, fibroblast growth factor receptors; FGFs, fibroblast growth factors; GAS6, growth-arrest-specific protein 6; HER, human epidermal receptor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IGF, insulin growth factor; IGF-1R, IGF-1 receptor; IGFBPs, IGF-binding proteins; IL, interleukin; IL-6R, IL-6 receptor; JAK, janus kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mechanisms; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; PDGFRs, platelet-derived growth factor receptors; PDGFs, platelet-derived growth factors; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase,catalytic subunit alpha; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; RAS, rat sarcoma; RTK, tyrosine kinase receptor; Resistance; SF, scatter factor; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; TKIs; TKIs, tyrosine kinase inhibitors; TKs, tyrosine kinases; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted therapies in development for non-small cell lung cancer.J Carcinog. 2013 Dec 31;12:22. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.123972. eCollection 2013. J Carcinog. 2013. PMID: 24574860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug resistance of targeted therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer harbored EGFR mutation: from mechanism analysis to clinical strategy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Dec;147(12):3653-3664. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03828-8. Epub 2021 Oct 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34661758 Review.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor and K-Ras mutations and resistance of lung cancer to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Cancer. 2012 Aug 15;118(16):3993-4003. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26656. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22359227 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors influence ABCG2 expression in EGFR-positive MDCK BCRP cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.ChemMedChem. 2012 Apr;7(4):650-62. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100543. Epub 2012 Feb 22. ChemMedChem. 2012. PMID: 22354538
Cited by
-
Analyzing and validating the prognostic value and mechanism of colon cancer immune microenvironment.J Transl Med. 2020 Aug 28;18(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02491-w. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32859214 Free PMC article.
-
The role of m6A methylation in targeted therapy resistance in lung cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 15;14(6):2994-3009. doi: 10.62347/LXOS2662. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39005690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factors STAT3 and MYC Are Key Players of Human Platelet Lysate-Induced Cell Proliferation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15782. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415782. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555426 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to bedside.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 21;24(27):2949-2973. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i27.2949. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30038463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CNTN-1 Upregulation Induced by Low-Dose Cisplatin Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Activation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Front Genet. 2022 May 27;13:891665. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.891665. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35711928 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

