Allosteric regulation of G protein-coupled receptor activity by phospholipids
- PMID: 26571351
- PMCID: PMC4718399
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1960
Allosteric regulation of G protein-coupled receptor activity by phospholipids
Abstract
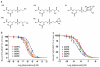
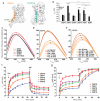
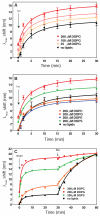
Lipids are emerging as key regulators of membrane protein structure and activity. These effects can be attributed either to the modification of bilayer properties (thickness, curvature and surface tension) or to the binding of specific lipids to the protein surface. For G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the effects of phospholipids on receptor structure and activity remain poorly understood. Here we reconstituted purified β2-adrenergic receptor (β2R) in high-density lipoparticles to systematically characterize the effect of biologically relevant phospholipids on receptor activity. We observed that the lipid headgroup type affected ligand binding (agonist and antagonist) and receptor activation. Specifically, phosphatidylgycerol markedly favored agonist binding and facilitated receptor activation, whereas phosphatidylethanolamine favored antagonist binding and stabilized the inactive state of the receptor. We then showed that these effects could be recapitulated with detergent-solubilized lipids, demonstrating that the functional modulation occurred in the absence of a bilayer. Our data suggest that phospholipids act as direct allosteric modulators of GPCR activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-Based Prediction of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Ligand Function: A β-Adrenoceptor Case Study.J Chem Inf Model. 2015 May 26;55(5):1045-61. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00066. Epub 2015 May 1. J Chem Inf Model. 2015. PMID: 25848966
-
Allosteric coupling from G protein to the agonist-binding pocket in GPCRs.Nature. 2016 Jul 7;535(7610):182-6. doi: 10.1038/nature18324. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27362234 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into positive and negative allosteric regulation of a G protein-coupled receptor through protein-lipid interactions.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 13;8(1):4456. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22735-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29535353 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational complexity of G-protein-coupled receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007 Aug;28(8):397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2007.06.003. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17629961 Review.
-
The role of conformational ensembles of seven transmembrane receptors in functional selectivity.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(6):775-81. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.09.004. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20933468 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanodisc-Tm: Rapid functional assessment of nanodisc reconstituted membrane proteins by CPM assay.MethodsX. 2016 Mar 14;3:212-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2016.03.009. eCollection 2016. MethodsX. 2016. PMID: 27054097 Free PMC article.
-
A sliding selectivity scale for lipid binding to membrane proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016 Aug;39:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27155089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Free Energies of Specific Protein Conformations Using the Martini Force Field.J Chem Theory Comput. 2024 Mar 12;20(5):2273-2283. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c01155. Epub 2024 Mar 1. J Chem Theory Comput. 2024. PMID: 38427574 Free PMC article.
-
Detergent-free isolation of CYP450-reductase's FMN-binding domain in E. coli lipid-nanodiscs using a charge-free polymer.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Apr 14;58(31):4913-4916. doi: 10.1039/d1cc07193a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 35356954 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the dynamic interplay between lipids and membrane proteins by hydrostatic pressure.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 1;13(1):1780. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29410-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35365643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee AG. Biological membranes: the importance of molecular detail. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011;36:493–500. - PubMed
-
- Gourdon P, et al. HiLiDe: Systematic Approach to Membrane Protein Crystallization in Lipid and Detergent. Crystal Growth & Design. 2011;11:2098–2106.
-
- Lee AG. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:62–87. - PubMed
-
- Hunte C, Richers S. Lipids and membrane protein structures. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008;18:406–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

