Soft, stretchable, fully implantable miniaturized optoelectronic systems for wireless optogenetics
- PMID: 26551059
- PMCID: PMC4880021
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3415
Soft, stretchable, fully implantable miniaturized optoelectronic systems for wireless optogenetics
Abstract
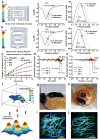
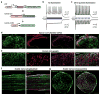
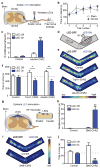
Optogenetics allows rapid, temporally specific control of neuronal activity by targeted expression and activation of light-sensitive proteins. Implementation typically requires remote light sources and fiber-optic delivery schemes that impose considerable physical constraints on natural behaviors. In this report we bypass these limitations using technologies that combine thin, mechanically soft neural interfaces with fully implantable, stretchable wireless radio power and control systems. The resulting devices achieve optogenetic modulation of the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. This is demonstrated with two form factors; stretchable film appliqués that interface directly with peripheral nerves, and flexible filaments that insert into the narrow confines of the spinal epidural space. These soft, thin devices are minimally invasive, and histological tests suggest they can be used in chronic studies. We demonstrate the power of this technology by modulating peripheral and spinal pain circuitry, providing evidence for the potential widespread use of these devices in research and future clinical applications of optogenetics outside the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests as defined by Nature Publishing Group, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and discussion reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stretchable multichannel antennas in soft wireless optoelectronic implants for optogenetics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 13;113(50):E8169-E8177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611769113. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27911798 Free PMC article.
-
Fully implantable, battery-free wireless optoelectronic devices for spinal optogenetics.Pain. 2017 Nov;158(11):2108-2116. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000968. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28700536 Free PMC article.
-
Monolithically Defined Wireless Fully Implantable Nervous System Interfaces.Acc Chem Res. 2024 May 7;57(9):1275-1286. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00013. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38608256
-
Multifunctional Fibers as Tools for Neuroscience and Neuroengineering.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Apr 17;51(4):829-838. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00558. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29561583 Review.
-
Soft, wireless and subdermally implantable recording and neuromodulation tools.J Neural Eng. 2021 Mar 17;18(4). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abe805. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 33607646 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Group-III Nitride Light-Emitting Diodes: From Millimeter to Micro-Nanometer Scales.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;15(10):1188. doi: 10.3390/mi15101188. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wireless multilateral devices for optogenetic studies of individual and social behaviors.Nat Neurosci. 2021 Jul;24(7):1035-1045. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00849-x. Epub 2021 May 10. Nat Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33972800 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of Optogenetic Methods and Their Application to Cardiac Experimental Systems.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 11;10:1096. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01096. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31572204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexible Temperature Sensors.Front Chem. 2021 Sep 22;9:539678. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.539678. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34631655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jun;20(6):330-345. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0140-6. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30833706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

