Chemokine Regulation of Neutrophil Infiltration of Skin Wounds
- PMID: 26543677
- PMCID: PMC4620531
- DOI: 10.1089/wound.2014.0559
Chemokine Regulation of Neutrophil Infiltration of Skin Wounds
Abstract
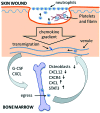
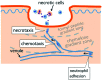
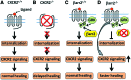
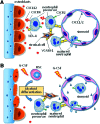
Significance: Efficient recruitment of neutrophils to an injured skin lesion is an important innate immune response for wound repair. Defects in neutrophil recruitment lead to impaired wound healing. Recent Advances: Chemokines and chemokine receptors are known to regulate neutrophil recruitment. Recent research advances reveal more mechanistic details about the regulation of chemokines and chemokine receptors on neutrophil egress from bone marrow, transmigration into the wound site, spatial navigation toward the necrotic skin tissue, and apoptosis-induced clearance by efferocytosis. Critical Issues: Skin injury triggers local and systemic alterations in the expression of multiple chemotactic molecules and the magnitude of chemokine receptor-mediated signaling. The responses of a number of CXC and CX3C chemokines and their receptors closely associate with the temporal and spatial recruitment of neutrophils to wound sites during the inflammatory phase and promote the clearance of necrotic neutrophils during the transition into the proliferative phase. Functional aberrancy in these chemokines and chemokine receptor systems is recognized as one of the important mechanisms underlying the pathology of impaired wound healing. Future Directions: Future research should aim to investigate the therapeutic modulation of neutrophil activity through the targeting of specific chemokines or chemokine receptors in the early inflammatory phase to improve clinical management of wound healing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemokines in cutaneous wound healing.J Leukoc Biol. 2001 Apr;69(4):513-21. J Leukoc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11310836 Review.
-
Chemokine regulation of neutrophil function in tumors.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Aug;30:81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 27021826 Review.
-
Bacterial clearance and survival are dependent on CXC chemokine receptor-2 ligands in a murine model of pulmonary Nocardia asteroides infection.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):908-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.908. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10623839
-
Chemokine regulation of neutrophil function in surgical inflammation.Arch Surg. 1999 Dec;134(12):1360-6. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.134.12.1360. Arch Surg. 1999. PMID: 10593335
-
A Broad-Spectrum Chemokine-Binding Protein of Bovine Papular Stomatitis Virus Inhibits Neutrophil and Monocyte Infiltration in Inflammatory and Wound Models of Mouse Skin.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0168007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168007. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936239 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Use of an Adjuvant System Improves Innate and Adaptive Immune Response When Associated with a Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis Antigen in a Vaccine Candidate against L. (Leishmania) infantum Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;11(2):395. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020395. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851272 Free PMC article.
-
Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective.Physiol Rev. 2019 Jan 1;99(1):665-706. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00067.2017. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30475656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of severity and subtype of fibrosing disease using model informed by inflammation and extracellular matrix gene index.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 23;15(10):e0240986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240986. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33095822 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Materials Promote Wound Healing through Modulation of Cell Behaviors.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Apr;9(10):e2105152. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105152. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35138042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine expression in human 3-dimensional cultured epidermis exposed to PM2.5 collected by cyclonic separation.Toxicol Res. 2022 Jul 14;39(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s43188-022-00142-4. eCollection 2023 Jan. Toxicol Res. 2022. PMID: 36726829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holzheimer RG, Steinmetz W. Local and systemic concentrations of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in human wounds. Eur J Med Res 2000;5:347–355 - PubMed
-
- Gaudry M, Bregerie O, Andrieu V, El Benna J, Pocidalo MA, Hakim J. Intracellular pool of vascular endothelial growth factor in human neutrophils. Blood 1997;90:4153–4161 - PubMed
-
- Wysocki AB, Staiano-Coico L, Grinnell F. Wound fluid from chronic leg ulcers contains elevated levels of metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. J Invest Dermatol 1993;101:64–68 - PubMed
-
- Koelink PJ, Overbeek SA, Braber S, et al. . Targeting chemokine receptors in chronic inflammatory diseases: an extensive review. Pharmacol Ther 2012;133:1–18 - PubMed
-
- Gillitzer R, Goebeler M. Chemokines in cutaneous wound healing. J Leukoc Biol 2001;69:513–521 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

