Improving chemotherapeutic efficiency in acute myeloid leukemia treatments by chemically synthesized peptide interfering with CXCR4/CXCL12 axis
- PMID: 26538086
- PMCID: PMC4633653
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16228
Improving chemotherapeutic efficiency in acute myeloid leukemia treatments by chemically synthesized peptide interfering with CXCR4/CXCL12 axis
Abstract
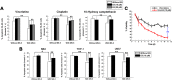
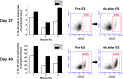
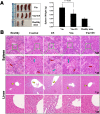
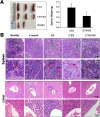
Bone marrow stroma can protect acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells against chemotherapeutic agents and provide anti-apoptosis and chemoresistance signals through secreting chemokine CXCL12 to activate its receptor CXCR4 on AML cells, resulting in minimal residual leukemia and relapse. Therefore disrupting the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis with antagonists is of great significance for improving chemosensitivity and decreasing relapse rate. In a previous study, we reported a novel synthetic peptide E5 with its remarkable effect on inhibiting CXCR4/CXCL12-mediated adhesion and migration of AML cells. Here we presented E5's capacity of enhancing the therapeutic efficiency of various chemotherapeutics on AML in vitro and in vivo. Results showed that E5 can diminish bone marrow stromal cell-provided protection to leukemia cells, significantly increasing the apoptosis induced by various chemotherapeutics in multiple AML cell lines. In an AML mouse xenograft model, E5 induced 1.84-fold increase of circulating AML cells out of protective stroma niche. Combined with vincristine or cyclophosphamide, E5 inhibited infiltration of AML cells into bone marrow, liver and spleen, as well as prolonged the lifespan of AML mice compared with mice treated with chemotherapy alone. In addition, E5 presented no toxicity in vivo according to the histological analysis and routine clinical parameters of serum analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A designed peptide targeting CXCR4 displays anti-acute myelocytic leukemia activity in vitro and in vivo.Sci Rep. 2014 Oct 14;4:6610. doi: 10.1038/srep06610. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25312253 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual-Function LipoAraN-E5 Coloaded with N4-Myristyloxycarbonyl-1-β-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine (AraN) and a CXCR4 Antagonistic Peptide (E5) for Blocking the Dissemination of Acute Myeloid Leukemia.ACS Nano. 2024 Oct 15;18(41):27917-27932. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c05079. Epub 2024 Oct 4. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39364559
-
TGF-β-Neutralizing Antibody 1D11 Enhances Cytarabine-Induced Apoptosis in AML Cells in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e62785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062785. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826077 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in acute myeloid leukaemia.Br J Haematol. 2020 Jun;189(5):815-825. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16456. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Br J Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32135579 Review.
-
Role of CXCR4 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia.Theranostics. 2013;3(1):34-9. doi: 10.7150/thno.5150. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Theranostics. 2013. PMID: 23382784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A biomimetic nanocomposite with enzyme-like activities and CXCR4 antagonism efficiently enhances the therapeutic efficacy of acute myeloid leukemia.Bioact Mater. 2022 Mar 31;18:526-538. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.03.022. eCollection 2022 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35415298 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow Aging and the Leukaemia-Induced Senescence of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Exploring Similarities.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 29;12(5):716. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050716. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting murine leukemic stem cells by antibody functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18932-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343865 Free PMC article.
-
The Bone Marrow Niche - The Tumor Microenvironment That Ensures Leukemia Progression.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:259-293. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32130704 Review.
-
A Nucleus-Targeting WT1 Antagonistic Peptide Encapsulated in Polymeric Nanomicelles Combats Refractory Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 12;15(9):2305. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092305. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Löwenberg B., Downing J. R. & Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 14, 1051–1062 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Tavor S. & Petit I. Can inhibition of the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis eradicate acute leukemia. Semin Cancer Biol. 20, 178–185 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Li Z. W. & Dalton W. S. Tumor microenvironment and drug resistance in hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev. 20, 333–342 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa F. et al. Chemotherapy-resistant human AML stem cells home to and engraft within the bone-marrow endosteal region. Nat Biotechnol. 25, 1315–1321 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Konopleva M. & Andreeff M. Targeting the leukemia microenvironment. Curr Drug Targets. 8, 685–701 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

