A Database of microRNA Expression Patterns in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 26506012
- PMCID: PMC4624429
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138313
A Database of microRNA Expression Patterns in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
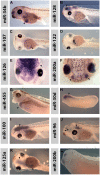
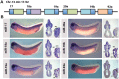
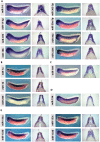
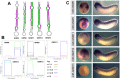
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNAs around 22 nucleotides long. They inhibit gene expression either by translational repression or by causing the degradation of the mRNAs they bind to. Many are highly conserved amongst diverse organisms and have restricted spatio-temporal expression patterns during embryonic development where they are thought to be involved in generating accuracy of developmental timing and in supporting cell fate decisions and tissue identity. We determined the expression patterns of 180 miRNAs in Xenopus laevis embryos using LNA oligonucleotides. In addition we carried out small RNA-seq on different stages of early Xenopus development, identified 44 miRNAs belonging to 29 new families and characterized the expression of 5 of these. Our analyses identified miRNA expression in many organs of the developing embryo. In particular a large number were expressed in neural tissue and in the somites. Surprisingly none of the miRNAs we have looked at show expression in the heart. Our results have been made freely available as a resource in both XenMARK and Xenbase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNAs associated with early neural crest development in Xenopus laevis.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 18;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4436-0. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29347911 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling the Messenger: Regulated Translation of Maternal mRNAs in Xenopus laevis Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;953:49-82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46095-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27975270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of microRNAs and microRNA targets in Xenopus gastrulae: The role of miR-26 in the regulation of Smad1.Dev Biol. 2016 Jan 1;409(1):26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26548531
-
Cloning and characterization of Xenopus laevis drg2, a member of the developmentally regulated GTP-binding protein subfamily.Gene. 2003 Dec 11;322:105-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2003.08.016. Gene. 2003. PMID: 14644502
-
Analysis of microRNA functions.Methods Cell Biol. 2019;151:323-334. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Methods Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30948016 Review.
Cited by
-
Short 2'-O-methyl/LNA oligomers as highly-selective inhibitors of miRNA production in vitro and in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jun 10;52(10):5804-5824. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae284. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38676942 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs associated with early neural crest development in Xenopus laevis.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 18;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4436-0. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29347911 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and differential regulation of microRNAs during thyroid hormone-dependent metamorphosis in Microhyla fissipes.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jun 28;19(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4848-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29954327 Free PMC article.
-
Interdigital tissue remodelling in the embryonic limb involves dynamic regulation of the miRNA profiles.J Anat. 2017 Aug;231(2):275-286. doi: 10.1111/joa.12629. Epub 2017 May 24. J Anat. 2017. PMID: 28543398 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient miRNA knockout approach using CRISPR-Cas9 in Xenopus.Dev Biol. 2022 Mar;483:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.12.015. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34968443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goljanek-Whysall K, Mok GF, Fahad Alrefaei A, Kennerley N, Wheeler GN, Munsterberg A. myomiR-dependent switching of BAF60 variant incorporation into Brg1 chromatin remodeling complexes during embryo myogenesis. Development (Cambridge, England). 2014;141(17):3378–87. 10.1242/dev.108787 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/H003525/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/D016444/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H003525/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

