CDDO-Me inhibits tumor growth and prevents recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 26497549
- PMCID: PMC4665937
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3212
CDDO-Me inhibits tumor growth and prevents recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
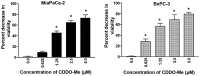
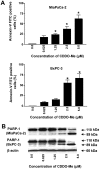
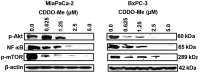
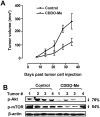
Methyl-2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oate (CDDO-Me) has shown potent antitumorigenic activity against a wide range of cancer cell lines in vitro and inhibited the growth of liver, lung and prostate cancer in vivo. In the present study, we examined the antitumor activity of CDDO-Me for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells with and without activating K-ras mutations. Treatment of K-ras mutant MiaPaCa-2 and K-ras normal BxPC-3 cells with CDDO-Me elicited strong antiproliferative and proapoptopic responses in both cell lines in culture. The inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis was accompanied by the inhibition of antiapoptotic/prosurvival p-Akt, NF-кB and p-mTOR signaling proteins. For testing efficacy of CDDO-Me in vivo heterotopic and orthotopic xenografts were generated by implanting BxPC-3 and MiaPaCa-2 cells subcutaneously and in the pancreatic tail, respectively. Treatment with CDDO-Me significantly inhibited the growth of BxPC-3 xenografts and reduced the levels of p-Akt and p-mTOR in tumor tissue. In mice with orthotopic MiaPaCa-2 xenografts, treatment with CDDO-Me prolonged the survival of mice when administered following the surgical resection of tumors. The latter was attributed to the eradication of residual PDAC remaining after resection of tumors. These preclinical data demonstrate the potential of CDDO-Me for treating primary PDAC tumors and for preventing relapse/recurrence through the destruction of residual disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by independently targeting pro-survival Akt and mTOR.Prostate. 2009 Jun 1;69(8):851-60. doi: 10.1002/pros.20937. Prostate. 2009. PMID: 19189297 Free PMC article.
-
CDDO-Me inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, down-regulates Akt, mTOR, NF-kappaB and NF-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and proangiogenic proteins in TRAMP prostate cancer cells.J Exp Ther Oncol. 2008;7(1):31-9. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18472640
-
Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis by CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent.J Exp Ther Oncol. 2012;10(1):51-64. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22946344 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, Two Derivatives of Natural Triterpenoids.Molecules. 2019 Nov 13;24(22):4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical evidences toward the use of triterpenoid CDDO-Me for solid cancer prevention and treatment.Mol Cancer. 2014 Feb 20;13:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-30. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24552536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Location, Orientation and Aggregation of Bardoxolone-ME, CDDO-ME, in a Complex Phospholipid Bilayer Membrane.J Membr Biol. 2020 Apr;253(2):115-128. doi: 10.1007/s00232-020-00106-5. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Membr Biol. 2020. PMID: 31965219
-
Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases.World J Clin Cases. 2020 May 26;8(10):1767-1792. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i10.1767. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 32518769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of natural products in revealing NRF2 function.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Jun 1;37(6):797-826. doi: 10.1039/c9np00061e. Epub 2020 May 13. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 32400766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multi-Faceted Consequences of NRF2 Activation throughout Carcinogenesis.Mol Cells. 2023 Mar 31;46(3):176-186. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2191. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36994476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding, diagnosing, and treating pancreatic cancer from the perspective of telomeres and telomerase.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Sep;31(9):1292-1305. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00768-6. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38594465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pancreatic Cancer-National Cancer Institute. U.S. National Institutes of Health. [Accessed April 6, 2010];Cancer Gov. http:www.cancer.gov/cancer-topics/types/pancreatic.
-
- Mulcahy MF, Wahl AO, Small W., Jr The current status of combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy for locally advanced or resected pancreas cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2005;3:637–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

