STATs: An Old Story, Yet Mesmerizing
- PMID: 26464811
- PMCID: PMC4601860
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2015.1
STATs: An Old Story, Yet Mesmerizing
Abstract
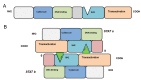
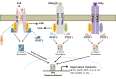
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) are cytoplasmic transcription factors that have a key role in cell fate. STATs, a protein family comprised of seven members, are proteins which are latent cytoplasmic transcription factors that convey signals from the cell surface to the nucleus through activation by cytokines and growth factors. The signaling pathways have diverse biological functions that include roles in cell differentiation, proliferation, development, apoptosis, and inflammation which place them at the center of a very active area of research. In this review we explain Janus kinase (JAK)/STAT signaling and focus on STAT3, which is transient from cytoplasm to nucleus after phosphorylation. This procedure controls fundamental biological processes by regulating nuclear genes controlling cell proliferation, survival, and development. In some hematopoietic disorders and cancers, overexpression and activation of STAT3 result in high proliferation, suppression of cell differentiation and inhibition of cell maturation. This article focuses on STAT3 and its role in malignancy, in addition to the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) on STAT3 activation in certain cancers.
Keywords: JAK; Malignancy; STAT; Signaling Pathways; miRNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IL-3 signaling and the role of Src kinases, JAKs and STATs: a covert liaison unveiled.Oncogene. 2000 May 15;19(21):2532-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203594. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10851052 Review.
-
Cell density dependent increase of constitutive signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activity in melanoma cells is mediated by Janus kinases.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Dec;5(12):1331-41. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0317. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18171991
-
JAKs, STATs and Src kinases in hematopoiesis.Oncogene. 2002 May 13;21(21):3334-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205398. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032773 Review.
-
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs): Novel targets of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006 Mar;6(2):107-21. doi: 10.2174/156800906776056491. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16529541 Review.
-
PDGF stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK 1 protein tyrosine kinase in human mesangial cells.Kidney Int. 1996 Jan;49(1):19-25. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.3. Kidney Int. 1996. PMID: 8770944
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 6;14(5):1001. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14051001. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35631587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bixin Protects Against Kidney Interstitial Fibrosis Through Promoting STAT6 Degradation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 17;8:576988. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.576988. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33313043 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Type of Blood Biomarker: Distinct Changes of Cytokine-Induced STAT Phosphorylation in Blood T Cells Between Colorectal Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 12;11(8):1157. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081157. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31409016 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein L31 (RPL31) inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 20;9(2):e13076. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13076. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36816257 Free PMC article.
-
Combined PARP inhibitors and small molecular inhibitors in solid tumor treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Feb;62(2):28. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5476. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36601757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schindler C, Shuai K, Prezioso VR, Darnell JE Jr. Interferondependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992;257(5071):809–813. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277(5332):1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa H, Mahmoud MS, Fujii R, Abroun S, Kawano MM. Proliferation of immature myeloma cells by interleukin6 is associated with CD45 expression in human multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;39(1-2):51–55. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
