ST2 blockade reduces sST2-producing T cells while maintaining protective mST2-expressing T cells during graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 26446957
- PMCID: PMC4699312
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aab0166
ST2 blockade reduces sST2-producing T cells while maintaining protective mST2-expressing T cells during graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) remains a devastating complication after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). We previously identified high plasma soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (sST2) as a biomarker of the development of GVHD and death. sST2 sequesters interleukin-33 (IL-33), limiting its availability to T cells expressing membrane-bound ST2 (mST2) [T helper 2 (TH2) cells and ST2(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells]. We report that blockade of sST2 in the peritransplant period with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody (anti-ST2 mAb) reduced GVHD severity and mortality. We identified intestinal stromal cells and T cells as major sources of sST2 during GVHD. ST2 blockade decreased systemic interferon-γ, IL-17, and IL-23 but increased IL-10 and IL-33 plasma levels. ST2 blockade also reduced sST2 production by IL-17-producing T cells while maintaining protective mST2-expressing T cells, increasing the frequency of intestinal myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and decreasing the frequency of intestinal CD103 dendritic cells. Finally, ST2 blockade preserved graft-versus-leukemia activity in a model of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia. Our findings suggest that ST2 is a therapeutic target for severe GVHD and that the ST2/IL-33 pathway could be investigated in other T cell-mediated immune disorders with loss of tolerance.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Paczesny has a patent on “Methods of detection of graft-versus-host disease” licensed to Viracor-IBT Laboratories. Otherwise, the authors have no other relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
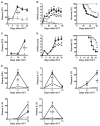
 ) or allogeneic B6 (
) or allogeneic B6 (
 ) BM cells (5 × 106) and splenic purified T cells (2 × 106). Soluble ST2 concentrations in plasma collected at indicated times post-HCT from C3H.SW recipients (unit: ng/mL) (p=0.0001; n=10–12; t-test). The data are from 4 independent experiments. (B) Clinical scores of GVHD and survival curves for C3H.SW mice receiving syngeneic (
) BM cells (5 × 106) and splenic purified T cells (2 × 106). Soluble ST2 concentrations in plasma collected at indicated times post-HCT from C3H.SW recipients (unit: ng/mL) (p=0.0001; n=10–12; t-test). The data are from 4 independent experiments. (B) Clinical scores of GVHD and survival curves for C3H.SW mice receiving syngeneic (
 ) or allogeneic B6 cells and treated with anti-mouse ST2 antibody (
) or allogeneic B6 cells and treated with anti-mouse ST2 antibody (
 ) or IgG control antibody (
) or IgG control antibody (
 ) at day -1 and day +1 post-HCT. The data are from 3 independent experiments (p values for GVHD scores are in Table S1, p=0.0256 for survival analysis; n=15–23 per group; t-test for GVHD score and Log-rank test for survival analysis). (C) Irradiated NSG mice (350 cGy) received 2.5 × 106 T cells purified from PBMCs of healthy donors (
) at day -1 and day +1 post-HCT. The data are from 3 independent experiments (p values for GVHD scores are in Table S1, p=0.0256 for survival analysis; n=15–23 per group; t-test for GVHD score and Log-rank test for survival analysis). (C) Irradiated NSG mice (350 cGy) received 2.5 × 106 T cells purified from PBMCs of healthy donors (
 ). The control group was irradiated without receiving human T cells (
). The control group was irradiated without receiving human T cells (
 ). Human soluble ST2 concentrations in plasma collected at indicated times post-HCT from NSG recipient mice with or without engrafted human T cells (unit: pg/mL). The data are from 3 independent experiments (p=0.0028; n=7–9 per group; t-test). (D) Clinical scores of GVHD and survival curves for NSG mice receiving human T cells and treated with anti-human and anti-mouse ST2 antibodies (
). Human soluble ST2 concentrations in plasma collected at indicated times post-HCT from NSG recipient mice with or without engrafted human T cells (unit: pg/mL). The data are from 3 independent experiments (p=0.0028; n=7–9 per group; t-test). (D) Clinical scores of GVHD and survival curves for NSG mice receiving human T cells and treated with anti-human and anti-mouse ST2 antibodies (
 ) or IgG control antibody (
) or IgG control antibody (
 ) every other day from day -1 to day +5 (4 doses) (p values for GVHD scores are in Table S1, p= 0.0329 for survival analysis; n=10 per group; t-test for GVHD score and Log-rank test for survival analysis). (E) IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-23, IL-10, and IL-33 concentrations in plasma collected every 5 days post-HCT from the B6→C3H.SW model (unit: pg/mL). The data are from 3 independent experiments. Syngeneic group (
) every other day from day -1 to day +5 (4 doses) (p values for GVHD scores are in Table S1, p= 0.0329 for survival analysis; n=10 per group; t-test for GVHD score and Log-rank test for survival analysis). (E) IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-23, IL-10, and IL-33 concentrations in plasma collected every 5 days post-HCT from the B6→C3H.SW model (unit: pg/mL). The data are from 3 independent experiments. Syngeneic group (
 ); allogeneic groups treated with anti-ST2 (
); allogeneic groups treated with anti-ST2 (
 ) or IgG control (
) or IgG control (
 ) (p values are in Table S1; n=3–9 per group, t-test).
) (p values are in Table S1; n=3–9 per group, t-test).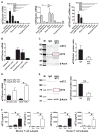

 ) or 2 × 106 WT (
) or 2 × 106 WT (
 ) or ST2−/− B6 T cells (
) or ST2−/− B6 T cells (
 ) (p=0.0289; n=6–10; Log-rank test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (E–G) Flow cytometric analysis at day 10 after allogeneic HCT shows percentages of intestinal CD4+ T cells expressing IFN-γ and Tbet (p=0.0173 for IFN-γ and p=0.0320 for Tbet; n=4; t-test) (E) and IL-17/IFN-γ, and RORγt (p=0.0273 for IL-17/IFN-γ and p=0.0273 for RORγt; n=4–5; t-test) (F) as well as Ki67 proliferation staining of cells expressing both IL-17 and IFN-γ (p=0.0088; n=4; t-test) (G). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (H) The bar graphs show the percentages of T cells expressing IL-4 or GATA3 from IgG-treated or anti-ST2-treated C3H.SW recipients mice at day 10 after allogeneic HCT, and the flow cytometry plots show mST2 expression on GATA3 T cells after IgG or anti-ST2 treatment. The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.0049 for IL-4 and p=0.0252 for GATA3; n=6; t-test). (I) IL-4 and GATA3-expressing T cells from C3H.SW recipient mice receiving WT or ST2−/− B6 T cells at day 10 after allogeneic HCT (p=0.0032 for IL-4 and p=0.0253 for GATA3; n=4; t-test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (J) The bar graphs show the percentages of intestinal T cells expressing FoxP3 from IgG-treated or anti-ST2-treated C3H.SW recipients mice at day 10 after allogeneic HCT, and the flow cytometry plots show mST2 expression on FoxP3 T cells after IgG or anti-ST2 treatment (p=0.0087; n=5; t-test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (K) FoxP3 and IL-10 expressing T cells from C3H.SW recipient mice receiving WT or ST2−/− B6 T cells at day 10 after allogeneic HCT. The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.0459 for FoxP3 and p=0.0471 for IL-10; n=4–5; t-test). (L) Survival curves for C3H.SW recipients mice transplanted with 5 × 106 B6 TCD BM cells plus either 2 × 105 WT (
) (p=0.0289; n=6–10; Log-rank test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (E–G) Flow cytometric analysis at day 10 after allogeneic HCT shows percentages of intestinal CD4+ T cells expressing IFN-γ and Tbet (p=0.0173 for IFN-γ and p=0.0320 for Tbet; n=4; t-test) (E) and IL-17/IFN-γ, and RORγt (p=0.0273 for IL-17/IFN-γ and p=0.0273 for RORγt; n=4–5; t-test) (F) as well as Ki67 proliferation staining of cells expressing both IL-17 and IFN-γ (p=0.0088; n=4; t-test) (G). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (H) The bar graphs show the percentages of T cells expressing IL-4 or GATA3 from IgG-treated or anti-ST2-treated C3H.SW recipients mice at day 10 after allogeneic HCT, and the flow cytometry plots show mST2 expression on GATA3 T cells after IgG or anti-ST2 treatment. The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.0049 for IL-4 and p=0.0252 for GATA3; n=6; t-test). (I) IL-4 and GATA3-expressing T cells from C3H.SW recipient mice receiving WT or ST2−/− B6 T cells at day 10 after allogeneic HCT (p=0.0032 for IL-4 and p=0.0253 for GATA3; n=4; t-test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (J) The bar graphs show the percentages of intestinal T cells expressing FoxP3 from IgG-treated or anti-ST2-treated C3H.SW recipients mice at day 10 after allogeneic HCT, and the flow cytometry plots show mST2 expression on FoxP3 T cells after IgG or anti-ST2 treatment (p=0.0087; n=5; t-test). The data are from 2 independent experiments. (K) FoxP3 and IL-10 expressing T cells from C3H.SW recipient mice receiving WT or ST2−/− B6 T cells at day 10 after allogeneic HCT. The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.0459 for FoxP3 and p=0.0471 for IL-10; n=4–5; t-test). (L) Survival curves for C3H.SW recipients mice transplanted with 5 × 106 B6 TCD BM cells plus either 2 × 105 WT (
 ) or ST2−/− B6 (
) or ST2−/− B6 (
 ) regulatory T cells (Tregs) with 2 × 106 WT B6 conventional T cells. (
) regulatory T cells (Tregs) with 2 × 106 WT B6 conventional T cells. (
 TCD BM only). The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.043; n=5–10 per group; Log-rank test). Flow cytometric gating strategies are in Fig. S10.
TCD BM only). The data are from 2 independent experiments (p=0.043; n=5–10 per group; Log-rank test). Flow cytometric gating strategies are in Fig. S10.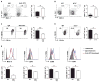
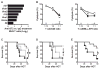
 ) or allogeneic HCT (B6→C3H.SW) treated with IgG control (
) or allogeneic HCT (B6→C3H.SW) treated with IgG control (
 ) or anti-ST2 mAb (
) or anti-ST2 mAb (
 ) (p=0.010; n=5–10 per group; Log-rank test). (D) Survival curves of C3H.SW mice receiving 104 GFP+ MLL-AF9 leukemic cells with syngeneic HCT C3H.SW→C3H.SW (
) (p=0.010; n=5–10 per group; Log-rank test). (D) Survival curves of C3H.SW mice receiving 104 GFP+ MLL-AF9 leukemic cells with syngeneic HCT C3H.SW→C3H.SW (
 ) or allogeneic HCT (B6→C3H.SW) treated with 6 doses (100 μg/dose, every other day from day -1 to day +9) of IgG control (
) or allogeneic HCT (B6→C3H.SW) treated with 6 doses (100 μg/dose, every other day from day -1 to day +9) of IgG control (
 ) or anti-ST2 mAb (
) or anti-ST2 mAb (
 ) (p=0.0357; n=4–5 per group; Log-rank test). (E) Survival curves of C3H.SW mice receiving 104 GFP+ MLL-AF9 leukemic cells with WT (
) (p=0.0357; n=4–5 per group; Log-rank test). (E) Survival curves of C3H.SW mice receiving 104 GFP+ MLL-AF9 leukemic cells with WT (
 ) or ST2−/− (
) or ST2−/− (
 ) B6 T cells (p=0.0203; n=6–10 per group; Log-rank test).
) B6 T cells (p=0.0203; n=6–10 per group; Log-rank test).Comment in
-
The emerging role of sST2 blocking in the therapy of graft-versus-host disease.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Oct;4(Suppl 1):S42. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.10.22. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27868010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prospects to translate the biology of IL-33 and ST2 during organ transplantation into therapeutics to treat graft-versus-host disease.Ann Transl Med. 2016 Dec;4(24):500. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.11.74. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 28149862 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The IL-33/ST2 axis augments effector T-cell responses during acute GVHD.Blood. 2015 May 14;125(20):3183-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-606830. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25814531 Free PMC article.
-
Rorc restrains the potency of ST2+ regulatory T cells in ameliorating intestinal graft-versus-host disease.JCI Insight. 2019 Mar 7;4(5):e122014. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.122014. eCollection 2019 Mar 7. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30694220 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-IL-12/23 p40 antibody attenuates experimental chronic graft-versus-host disease via suppression of IFN-γ/IL-17-producing cells.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 1;194(3):1357-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400973. Epub 2014 Dec 19. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25527789
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell graft manipulation as a mechanism of immunotherapy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2003 Aug;3(8):1121-43. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5769(03)00014-6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12860168 Review.
Cited by
-
Early inflammatory markers as prognostic indicators following allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1332777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332777. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38235129 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker Panel for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug 1;34(22):2583-90. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9615. Epub 2016 May 23. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27217465 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Cytokine IL-33 Modulates the Cytotoxic CD8 T Lymphocyte Activity During Nutrient Deprivation by Regulation of Lineage-Specific Differentiation Programs.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 24;10:1698. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01698. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31396219 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 Augments Virus-Specific Memory T Cell Inflation and Potentiates the Efficacy of an Attenuated Cytomegalovirus-Based Vaccine.J Immunol. 2019 Feb 1;202(3):943-955. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701757. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30635396 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) and the Potential of Novel Biomarkers in Optimizing Management of Acute and Chronic Graft vs. Host Disease (GvHD).Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 31;11:81. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00081. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32082329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu CJ, Ritz J. Induction of tumor immunity following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Adv Immunol. 2006;90:133–173. - PubMed
-
- Kolb HJ. Graft-versus-leukemia effects of transplantation and donor lymphocytes. Blood. 2008;112:4371–4383. - PubMed
-
- Shlomchik WD. Graft-versus-host disease. Nature reviews Immunology. 2007;7:340–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

