The Influence of CKD on Colonic Microbial Metabolism
- PMID: 26400570
- PMCID: PMC4849823
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015030279
The Influence of CKD on Colonic Microbial Metabolism
Abstract
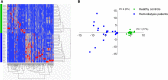
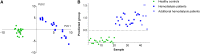
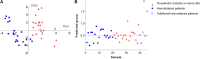
There is increasing interest in the colonic microbiota as a relevant source of uremic retention solutes accumulating in CKD. Renal disease can also profoundly affect the colonic microenvironment and has been associated with a distinct colonic microbial composition. However, the influence of CKD on the colonic microbial metabolism is largely unknown. Therefore, we studied fecal metabolite profiles of hemodialysis patients and healthy controls using a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method. We observed a clear discrimination between both groups, with 81 fecal volatile organic compounds detected at significantly different levels in hemodialysis patients and healthy controls. To further explore the differential impact of renal function loss per se versus the effect of dietary and other CKD-related factors, we also compared fecal metabolite profiles between patients on hemodialysis and household contacts on the same diet, which revealed a close resemblance. In contrast, significant differences were noted between the fecal samples of rats 6 weeks after 5/6th nephrectomy and those of sham-operated rats, still suggesting an independent influence of renal function loss. Thus, CKD associates with a distinct colonic microbial metabolism, although the effect of renal function loss per se in humans may be inferior to the effects of dietary and other CKD-related factors. The potential beneficial effect of therapeutics targeting colonic microbiota in patients with CKD remains to be examined.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; intestine; nutrition.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emodin via colonic irrigation modulates gut microbiota and reduces uremic toxins in rats with chronic kidney disease.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):17468-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8160. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27003359 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Prebiotic Arabinoxylan Oligosaccharides on Microbiota Derived Uremic Retention Solutes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0153893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153893. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100399 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of renal transplantation on retained microbial-human co-metabolites.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Oct;31(10):1721-1729. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw009. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26961998
-
Derangements in phosphate metabolism in chronic kidney diseases/endstage renal disease: therapeutic considerations.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011 Mar;18(2):120-31. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2011.02.004. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21406297 Review.
-
What would you like to eat, Mr CKD Microbiota? A Mediterranean Diet, please!Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014;39(2-3):114-23. doi: 10.1159/000355785. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014. PMID: 25117687 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-Based Diets, the Gut Microbiota, and Trimethylamine N-Oxide Production in Chronic Kidney Disease: Therapeutic Potential and Methodological Considerations.J Ren Nutr. 2021 Mar;31(2):121-131. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2020.04.007. Epub 2020 Jun 29. J Ren Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32616440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut-Derived Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 11;12(9):590. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090590. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32932981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota in renal physiology: focus on short-chain fatty acids and their receptors.Kidney Int. 2016 Dec;90(6):1191-1198. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.06.033. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27575555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites in vascular inflammation and cardiovascular disease.Amino Acids. 2022 Oct;54(10):1339-1356. doi: 10.1007/s00726-022-03161-5. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Amino Acids. 2022. PMID: 35451695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabonomic strategy for the detection of metabolic effects of probiotics combined with prebiotic supplementation in weaned rats.RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 30;8(9):5042-5057. doi: 10.1039/c7ra12067b. eCollection 2018 Jan 24. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shanahan F: The gut microbiota in 2011: Translating the microbiota to medicine. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9: 72–74, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Meyer TW, Hostetter TH: Uremic solutes from colon microbes. Kidney Int 81: 949–954, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Evenepoel P, Meijers BK, Bammens BR, Verbeke K: Uremic toxins originating from colonic microbial metabolism. Kidney Int Suppl 114: S12–S19, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

